Analog inputs is connectors for analog signal (guitar, microphone, sinthesizer) incoming to audio card.

If you buy "AuI ConverteR PROduce-RD" (2023/12.x version) from 24 August 2023 to 24 October 2023, you will get free update to version 2024 (13.x) after its release.
The beginning of articles about sound cards here...
1. Line input is connector for input to sound card signals with standard level (250 millivolts = 250 mV = 0.25 volts). Sources: output mixer, synthesizer, tape, CD-player, etc.
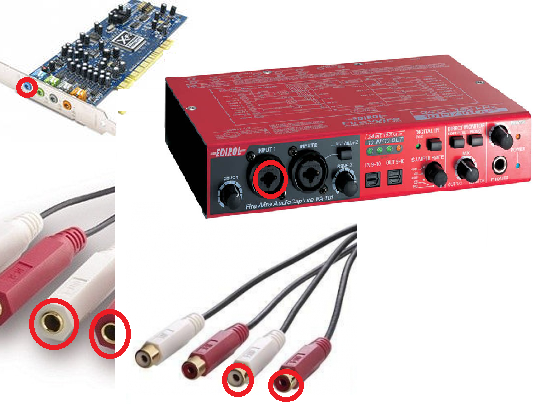

2. Microphone input Signal from mic input is amplified by microphone preamplifier.

Microphones divided two types: dynamic and condenser (electret).
Microphone output signal is very weak. So we will not hear microphone connected to line input. Some condenser microphones have internal preamp.
Dynamic microphone does not need power. Amateur electret microphones are often powered by batteries, placed in the microphone.
Impedance of mic input is 600 Ohm.
Professional condenser microphones require feeding a so-called phantom power 48 V.

Phantom power is supply voltage passed audio signal wires.
Therefore, if you are going to use a condenser microphone, there are 2 options:
a) Buy sound card with integrated microphone preamplifier supporting phantom power.
b) If the card has only line outputs, you have to purchase a mic preamp that provides phantom power.

3. Instrumental input (Hi-Z) is connector for guitar or bass guitar. It allows more fully consistent sound card impedance with guitar pickups for whole frequency range (more uniform frequency response).
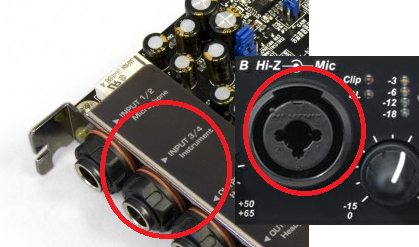
Required number of inputs is determined how much you want to record sound sources simultaneously. You can record on one instrument in series or playing simultaneously several parties: vocal group or acoustic drum set, various drums and cymbals are written with several individual microphones.
Read what is analog output here...