
If you buy "AuI ConverteR PROduce-RD" (2023/12.x version) from 24 August 2023 to 24 October 2023, you will get free update to version 2024 (13.x) after its release.
Audio Basis - articles about audio
Probably, you have heard not once about the ringing in audio. It’s a type of distortion. The ringing does not look good at plots. It may be clearly visible for musical instruments with a sharp attack: piano, guitar, drums, etc. What is audio ringing? Why it appears? Is it true that bad for sound quality? Should we reduce this artifact? Keep reading.
What is ringing audio
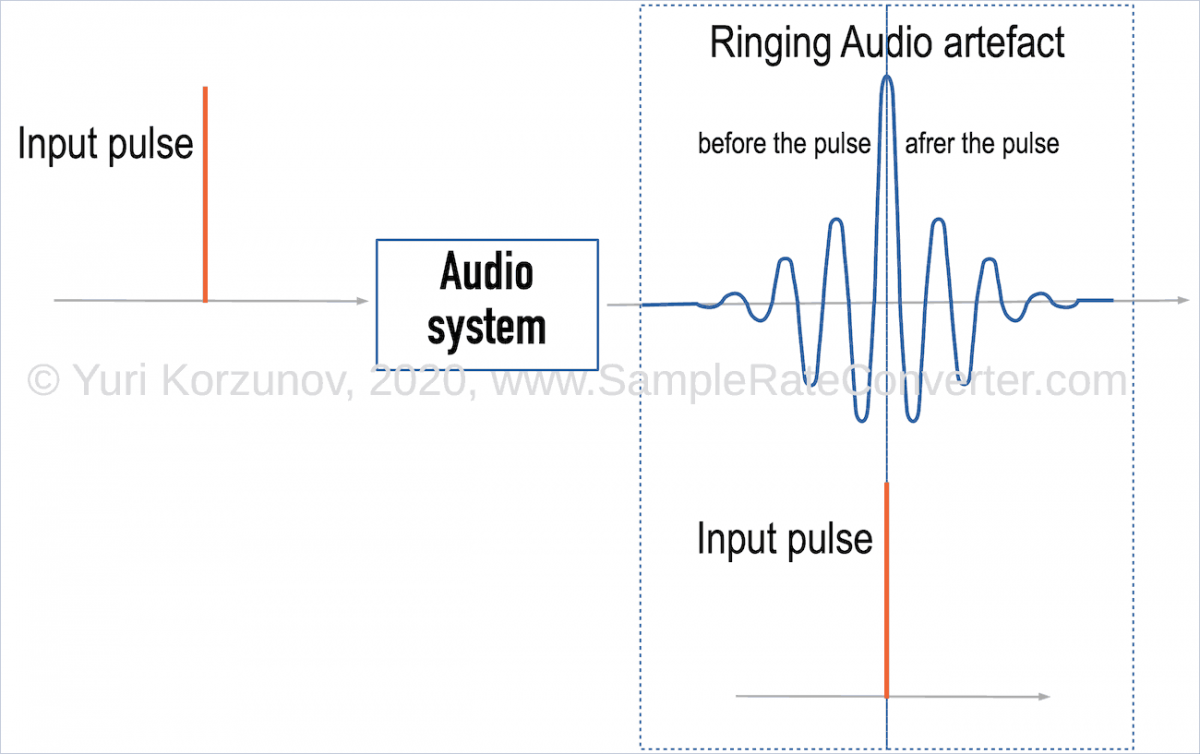
Ringing audio is artifacts of the output response of an audio device or a DSP algorithm (software/firmware), which is caused by input signal. These artifacts look like damped oscillations.
The reference input signal for ringing measurement is delta pulse (Dirac delta function).
In the theory, it's a signal with infinite high amplitude during an infinitely short time.
For digital-system measurements, that test pulse is 1 sample with maximum amplitude.
Analog input test pulse should have minimum durations that tend to be zero.
The ideal output signal should be similar to the input signal.
But elements of the system have digital filters and/or feedback.
Ringing in simple words
Let's imagine a security box with a transporter in an airport.
If we put a metal cube on the band at the box input, at the output we should get the cube. It's the ideal system.
If inside the box, hit the cube with a metal hummer, at the output we get the sounding cube. It will sound some time. And. it's a real system.
Ringing is output oscillations, that should not be for an ideal audio system.
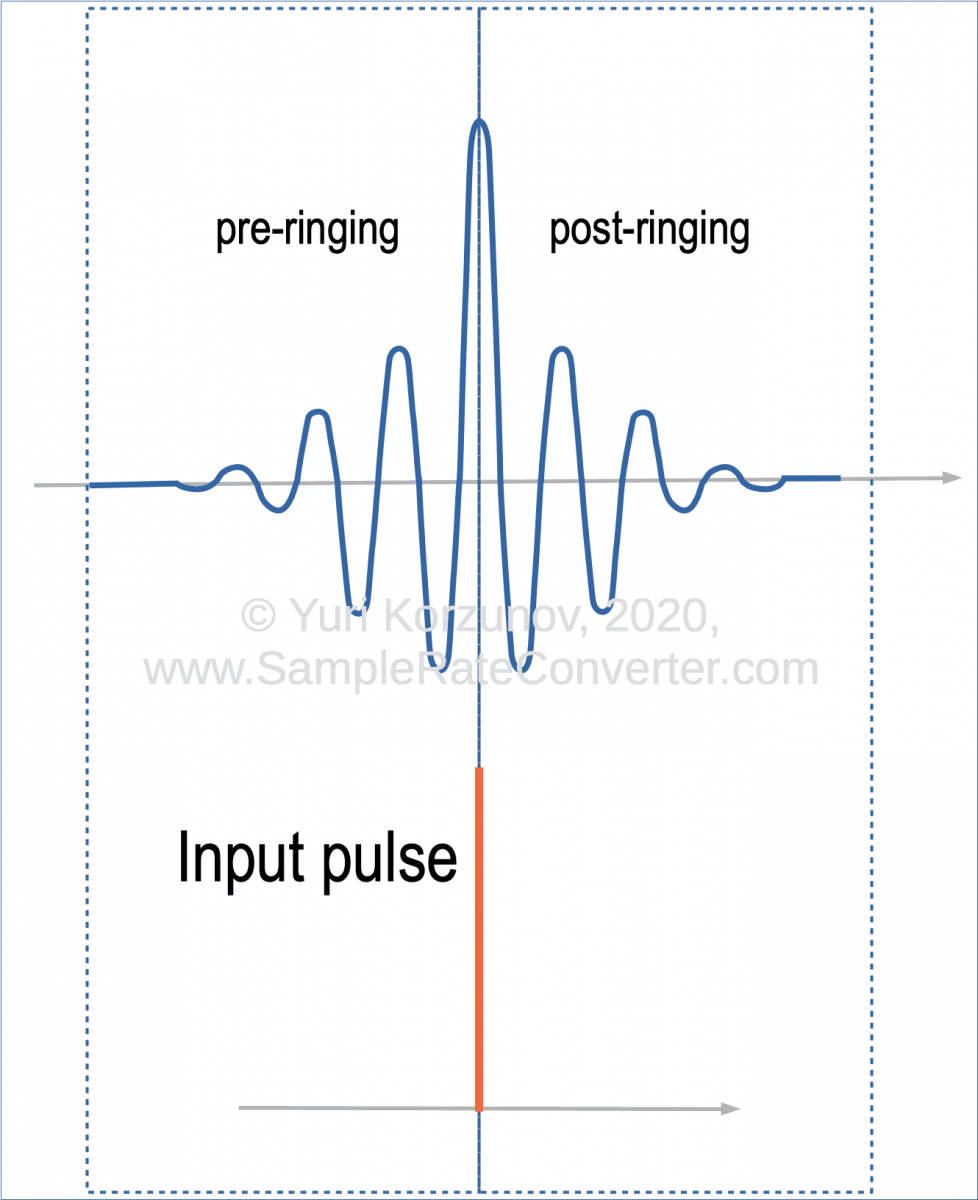
In the time after the input pulse (see drawing above), we can observe post-ringing. It's like an "echo".
In the time before the input pulse, we can observe pre-ringing. It's like a "backward echo".
What is ringing frequency?
We put a 1-sample pulse on a filter input. At the filter output, oscillation happens.
The ringing frequency is the oscillation frequency.
The filter has some magnitude-phase (level-time delay) response for an input sine.
Magnitude-phase responses for all input sines are called "magnitude-phase response of filter".
It shows what frequencies filter pass or suppress.
The magnitude-phase response of the filter defines the oscillation frequency.
Back to top
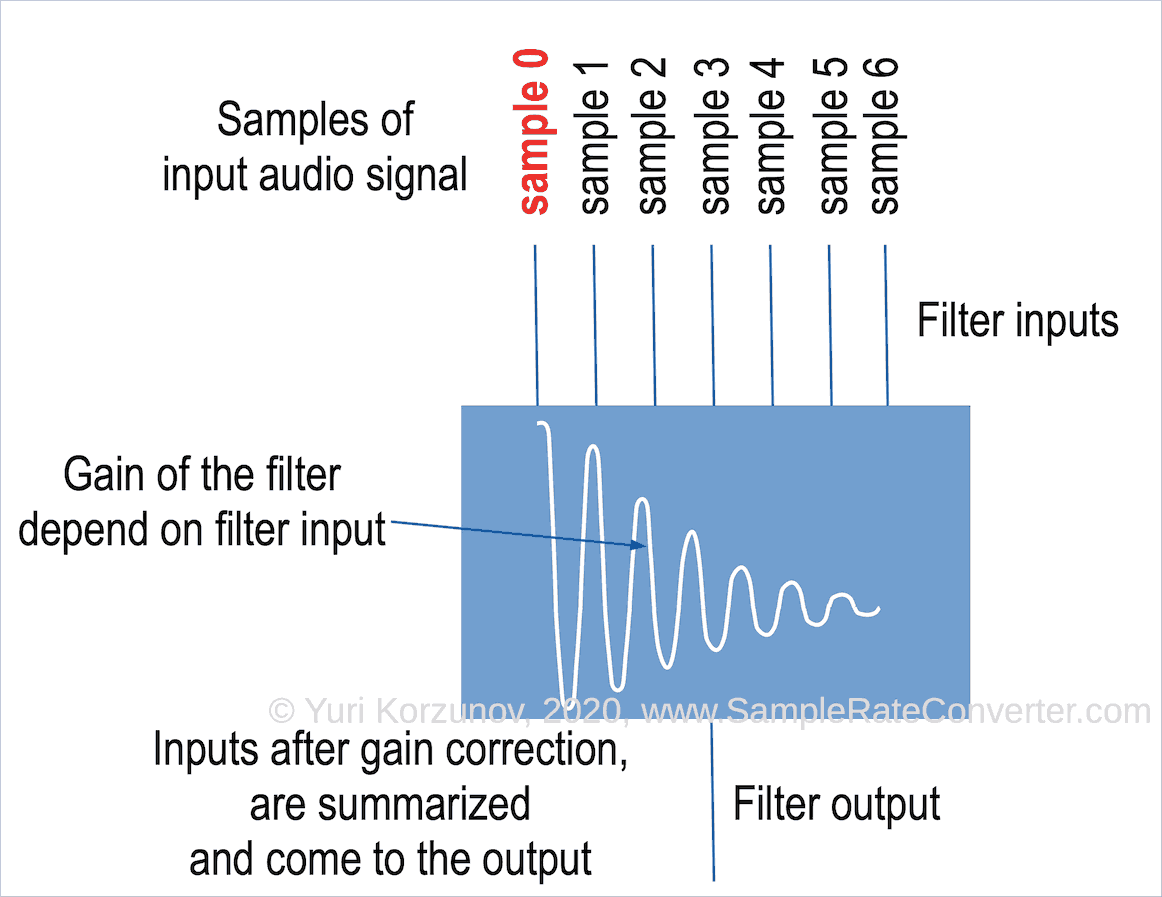
How digital filter works
A digital filter unit can cause ringing.
The unit:
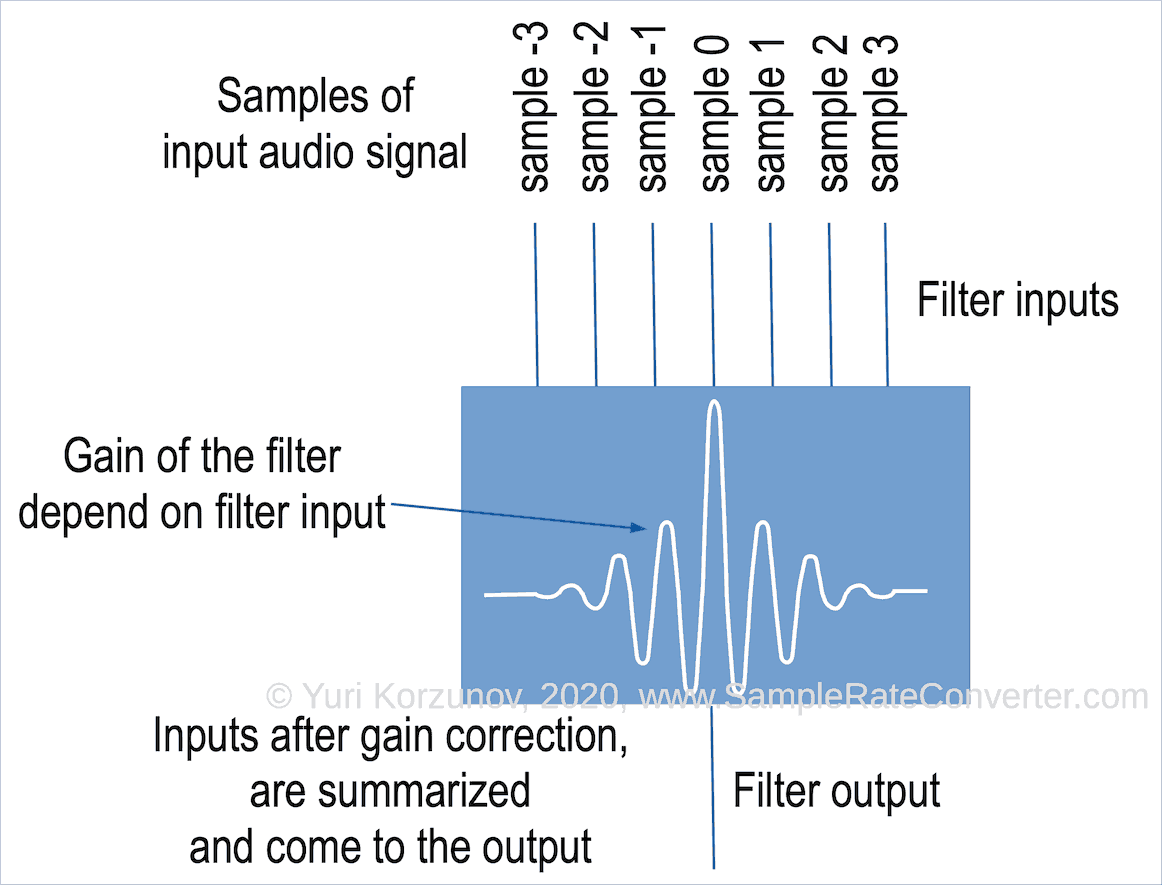
- Filter receives several sequential samples of digital audio signal. The signals come to the filter inputs.
- Filter applies individual gain (tap) for each of the samples.
- Filter summarizes values from goal 2 and sends it to 1 output. The output value is the next output sample.
If we consider filter as a unit, it has 1 input and 1 output.
A digital signal comes to the input. And other signal exists from the output.
Actually, filter catches several samples at the input.
After it, the unit:
- shifts along 1 sample of the input signal and
- perform the steps from 1 to 3.
I.e. the filter inputs slide along the processed samples of the input signal.
Back to top
Linear phase filter
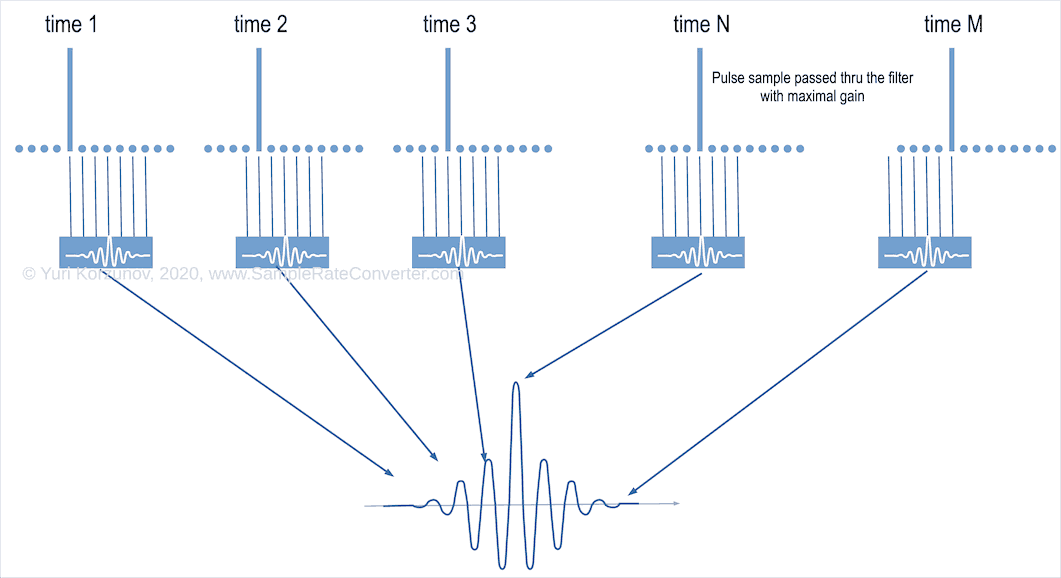
As we told above, to calculate an output sample, a digital filter takes several sequential input samples. The maximum amplitude at the output rise when the pulse's sample will at the middle of the inputs (taps). It's shown in the picture below (time N).
So, we can consider time N as a moment of pulse rising at the output.
What is pre-ringing?
But in previous moment time 1, when pulse's sample comes to the most left input with minimum gain, non-zero level rise at the filter output.
So, we can view the non-zero output level by the input pulse, before it comes to output in maximum level (time N).
When the pulse's sample comes to the second input with higher gain, it produces a higher non-zero output level (time 2). And, same way, up to time N when pulse achieved tap with maximum gain.
Oscillations (distortions) at the output [before actual pulse moment (time N)] are called as pre-ringing.
Post-ringing
Post-ringing is the opposite effect. When pulse moves from the input with maximum gain to the most right input with minimum gain, non-zero levels rise at the filter output.
It happens after pulse's actual moment at the output (time N). I.e. already no signal at the output, but oscillations, still, are there.
Minimum phase filter
From an analog-system point of view, pre-ringing is a "strange" issue enough.
Still no signal but its artefacts are there.
To solve the issue, a minimum phase filter was invented.
However, minimum phase filter have own issues.
Minimum vs linear phase filter
Minimum vs linear phase filter
| Linear | Minimum phase | |
|---|---|---|
| Magnitude-frequency response | identical for both ones | |
| Phase-frequency response | linear | non-linear |
| Pre-ringing | yes | no |
| Post-ringing | yes | yes |
| Post-ringing energy | Higher than post-ringing energy of linear phase filter | |
A minimum phase filter has a non-linear phase into the passband. Non-linearity degree depends on filtering unit implementation.
Back to topRinging and magnitude-frequency response
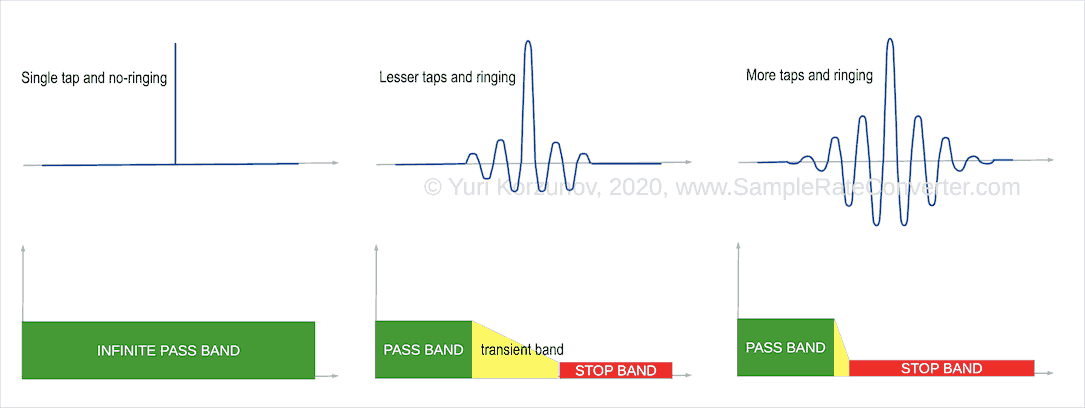
For example, we consider a low-frequency filter, that is very popular in audio. Other filtering types have same properties.
Low-frequency filter has passband at low frequencies and stopband at high ones.
Between these bands, transient band is placed.
when pulse at the input
To keep the maximum signal band after resampling, the transient band should have zero width.
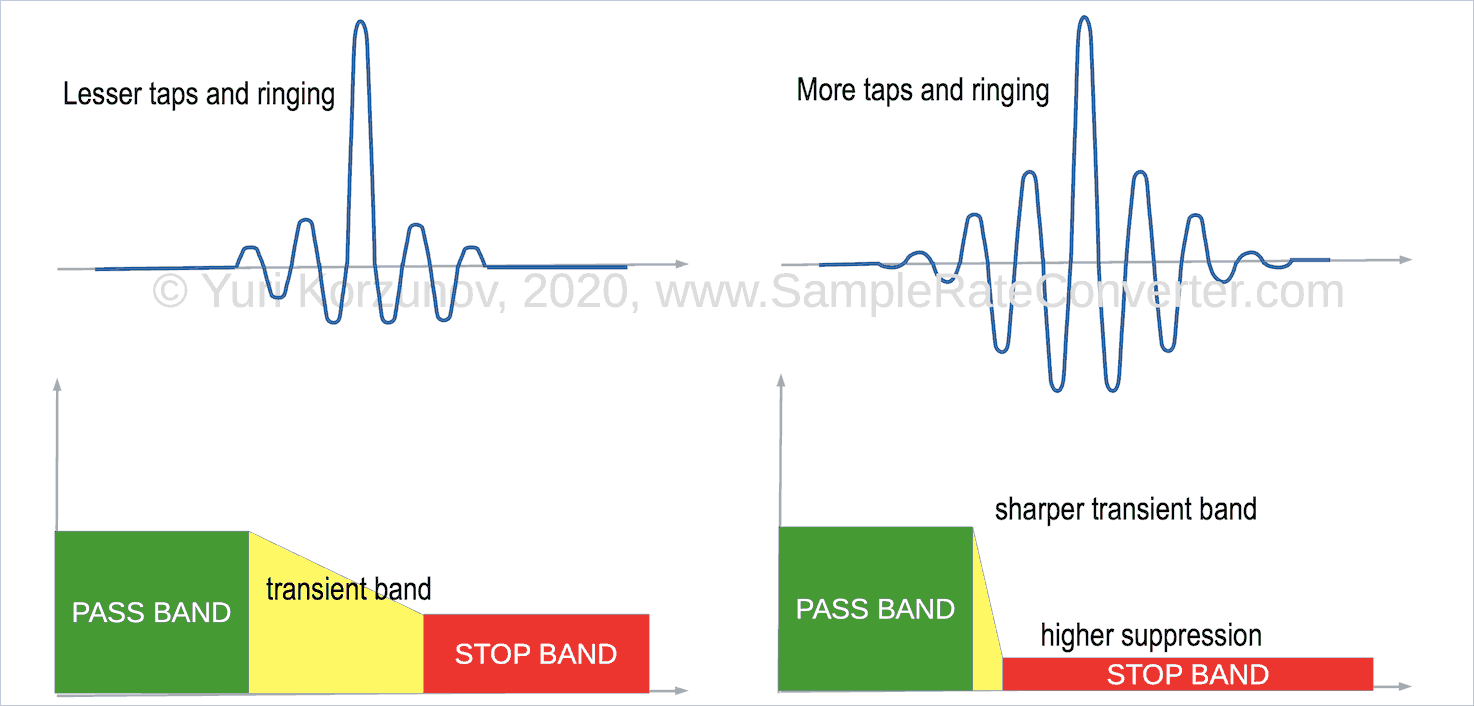
But the band minimization requires more taps (see above: filter inputs). And higher tap number causes the longer length of ringing (see picture "Ringing audio of linear phase filter").
It is fairly for the minimum phase one too.
When the audio system (digital or analog) has a flat amplitude-frequency response from 0 to Infinity Hz, no ringing is there.
Many sampling rate conversion algorithms use resampling filters.
For the qualitative rejection of conversion artefacts and minimum losses of the passband width:
- the filtering unit should have a minimum width of transient band; and
- the transient band should be below half of the sampling rate.
Sharpness (width) of the transient band depend on the suppression level at stopband. The suppression level defines distortion level into useful (including audible) band after resampling.
But filtering unit with narrower transition band (higher its sharpness) has higher energy of the ringing oscillations out of the time of input pulse.
NOTE: these bandwidths of a digital filter are considered in relative coordinated. As rule, total bandwidth is considered as 1.0. And the bandwidths are in range 0.0 ... 1.0.
The widths and ringing lenght (in samples) don't depend on sample rate.
Sound quality
The author has no information about proper studies of real ringing effect in low or high pass and other filters impact to sound quality.
In the general case, ringing is not so scary, as it seems at the response to the pulse plot.
To achieve this effect, the difference between neighbor samples should be close to maximum possible value.
But, in most cases, the difference is too small.
And the ringing level is very low too.
For sharp-attack waveforms (piano, guitar, drums, etc.), ringing may be visible even.
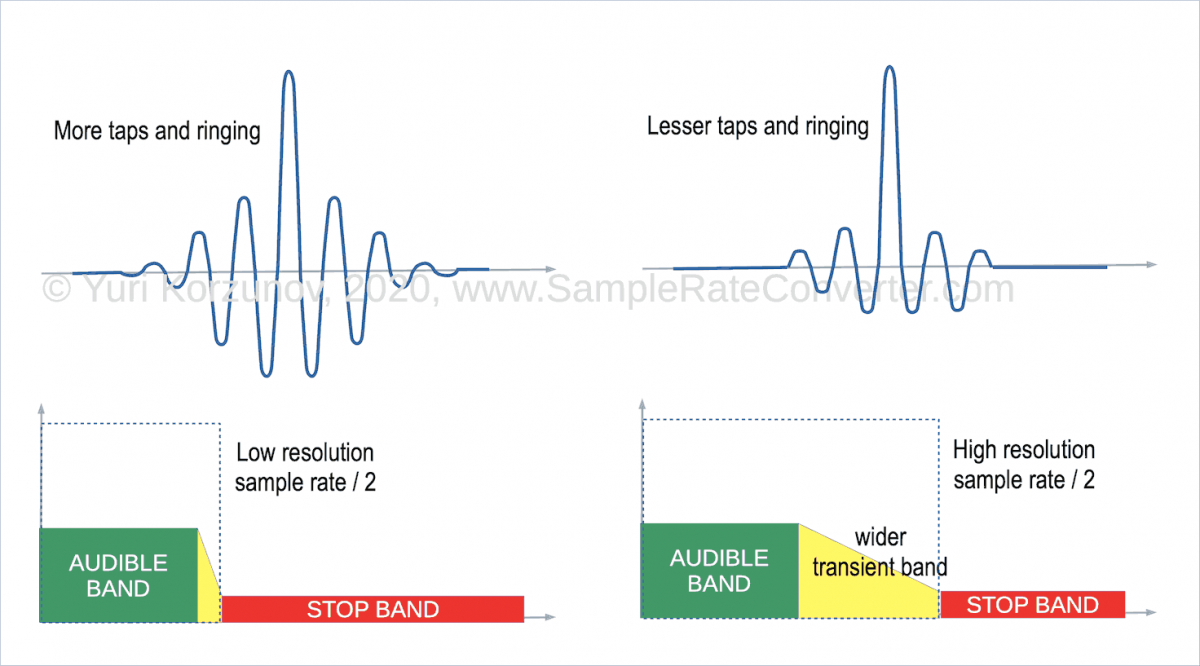
Anyway, high resolution of musical signals allows using a wider transient band and keep artefact suppression.
The actual audible range is up to 20 kHz. High resolution has a higher band.
So resampling and other filters may start transient band from 20 kHz.
A higher sampling rate allows to reduce the sharpness of the transient band and keeps stopband.
Lesser sharpness reduces tap number and ringing.
Back to top
Apodizing filter
How to reduce ringing in circuit of filter? Which filter does not produce ringing effect?
Audio device and software designers strive to reduce or rid of the ringing.
One of the examples is an apodizing filter. For input pulse, it should provide output response without oscillations. As example, it may be implemented as some expanding of the pulse in time at the output.
However, the backside of the improvement is the lesser sharpness of the transient band. In some cases, it can cause audible aliases due to sampling rate limitation. However, high-resolution may solve (or partially solve) sharpness-aliases issue.
Back to top
Conclusions
In digital filtering, ringing audio is unavoidable artefacts. Only filter optimization may be applied to save balance between:
- lower ringing;
- narrower transient band (or wider passband);
- artefacts due to a lack of suppression in the stopband.
The author knows nothing about proper researches of ringing impact to sound quality.
In majority of musical signal types, ringing levels are below noise floor. And we don't even have consider the artefacts there.
In general case of audio device/software design, ringing-audio reducing may be recommended.
Author: Yuri Korzunov,
Audiophile Inventory's developer
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes ringing in a circuit?
In electrical and electronical circuits, all conductors (wires) have physical sizes. It causes unwanted capacity and inductance. It may cause ringing for transient processes (oscillations or "the ringing") when electrical voltage in the circuit is changed.
Which filter has ringing effect?
Any filter has transient processes at its output when input signal is changed. In instance, input sine changes amplitude or frequency.
However, pre-ringing is digital filter feature only.
Read more...
What is ideal low-pass filter?
Ideal low-pass filter is so-called "brickwall" filter. Such filter has no transient band.
If you want to reduce ringing energy, you're need to expand transient band.
Read more...
Back to top
Read more
- What is Jitter in Audio. Sound Quality Issues >
- 64-bit audio processing. Necessity or redundancy >
- What is Audio Converter >
- How to Choose the Best Audio Converter Software >
- What is dithering audio? >
- Bit-Depth Audio and Harmonic Distortions >
- Audio as Optics >
- What is optimization audio for DAC >
- Where is the Limit of Audio Quality? >
- Power Conditioner for Audio. It's real advantage? >
Back to top

![What Is Ringing Audio [Definitive Guide] What Is Ringing Audio [Definitive Guide]](/sites/default/files/u1/what-ringing-audio.png)