If you buy "AuI ConverteR PROduce-RD" (2023/12.x version) from 24 August 2023 to 24 October 2023, you will get free update to version 2024 (13.x) after its release.
Audio Basis - articles about audio
Delta-sigma modulation for high resolution audio it's 1-bit (digital) stream of 0 and 1. Thus coded audio signal. The format used for storing DSF, DFF and ISO [1-bit HD audio].
Back to top
What is sigma-delta modulation in audio (DSD)?
Unlike multibit (16, 24, ... bit) modulation with "low" sampling frequencies (44, 48, ... kHz), sigma delta modulation (DSD audio) has super high sample rates:
1. 44 kHz x64(D64) = 2.8 MHz,
2. 44 kHz x128(D128) = 5.6 MHz.
Thus compensated for the loss of information due reducing of sample bit depth from 16 or 24 bit to 1.
Back to topHow sigma-delta modulator works
We will consider the conversion of multibit audio PCM (CD audio, audio files WAV, FLAC, AIFF, ...) to 1-bit audio files (DSF, DFF) using sigma delta modulation.
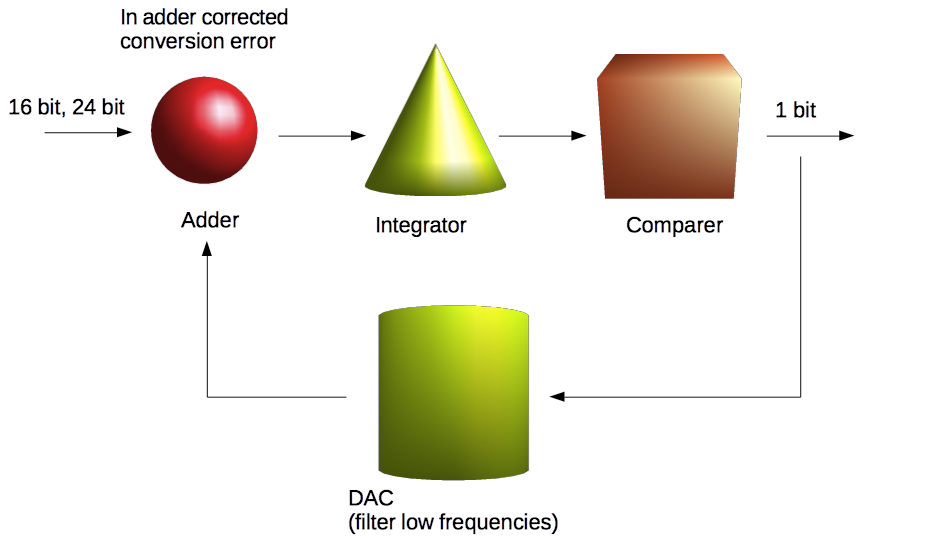
Sigma delta modulator inside
1. Delta-sigma modulator first integrates a multibit (input) signal (passes through an integrator [Low Frequency Pass Filter - LF]).
2. Output multilevel signal from integrator output divided to 1 and 0 (more zero / less zero). This is delta sigma modulated signal.
3. For decreasing of error output signal, it converted back to multilevel (multibit PCM like "analog signal") signal into DAC. Multilevel PCM signal from DAC subtracts from input PCM signal. So corrected output (from delta sigma modulator) signal. It (when will demodulated) will more approach to input signal.
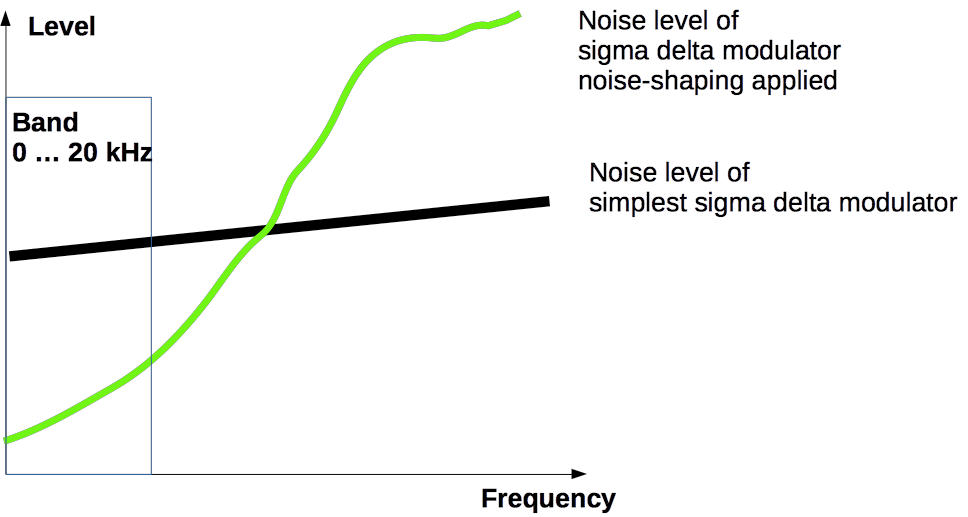
4. At output of demodulator appear 1 and 0 sequence.Its spectrum is useful audio signal (into band 0 ... 20 kHz) and noise with level -47 dB (for simplest modulator with sampling rate 44100 Hz x 64).
Thus, if pass the sequence of 1 and 0 through the low pass filter (0 ... 20 kHz), we distinguish the input signal. But in the spectral range of the useful signal (0 ... 20 kHz) will present the same noise with level -47 dB. Therefore impossible use this signal for high qualitative audio.
5. For reducing noise level into band 0 ... 20 kHz we can:
5.1. Increase sample rate. But it is not effective - increasing sample rate 2 times decrease noise level at 6 dB.
5.2. Apply noise shaping. Noise shaping extrudes noise energy out if band 0 ... 20 kHz. It decrease noise level to -145 дБ. It is compable for high resolution audio.
DAC for 1-bit sigma delta modulator is low frequency filter. It suppress concentrated by noise shaping energy out of band 0 ... 20 kHz. Thus we get high qualitative audio signal into band 0 ... 20 kHz.
For experiments with sigma delta modulation you can use free version of HD audio file converter AuI ConverteR 48x44 for convertation PCM to DSF and contrariwise.
- What is DSD audio >
- DSD vs. PCM. Real competitors? >
- DSD Decoder Audio >
- How work sigma delta modulation in audio >
- DSD Converter of Audio Files: What Inside? >
- What is Audio Formats DSD 2.8 DSD64 DSD5.6 DSD128 DSD256 DSD512 DSD1024 >
- DSD vs DSF vs DFF Files Audio. What is difference >
- DSD Editor [How it work, Sound quality issues] >
Back to top