In the audiophile’s quest for sonic perfection, the sample rate converter emerges as the unsung hero. Picture this: a landscape of devices, each with its own acoustic dialect of sampling rates. Some recordings are vast, stretching beyond the native range of our beloved gadgets. Others, we yearn to experience at the zenith of our device’s capabilities.
Here’s where the magic happens. A professional sample rate converter deftly navigates this terrain, minimizing losses to a whisper during DSD to DSD, and DSD to PCM conversions. It’s akin to an expert translator who captures the nuance of poetry across languages. The result? A sound so pure, so close to the original, it’s almost indistinguishable.
For the discerning ear, these minute details matter. The converter should not just change data—it should preserve the soul of the music to the maximum extent possible. Whether it's the warmth of a vinyl record or the clarity of a studio master, the right sample rate converter tries to ensure every listening session is an auditory feast. Keep reading for details.

If you buy "AuI ConverteR PROduce-RD" (2023/12.x version) from 24 August 2023 to 24 October 2023, you will get free update to version 2024 (13.x) after its release.

What does converting sample rate do?
Sample rate is a sample (frame) number per second. A higher sample rate means more samples per second.
An audio sample rate converter alters the time interval between samples of a digital signal. The signal is not changed. The time frame is changed. Samples are recalculated to keep unchanged content of the digital signal.
Back to topWhy Use a Sample Rate Converter?
Change the sample rate to make audio recordings work with your music player. For example, you can convert the sample rate for better sound from your digital-to-analog converter. Or, you can modify the sampling frequency of a recording to ensure compatibility with your favorite player.
You can convert the sample rate as the music plays or before you listen to it: change the audio quality of files beforehand.
For example, a computer can make different sounds work together by setting them to one sample rate. This lets you use one DAC to play a mix of sounds.
Audio devices usually work with these sample rates:
- For CDs: 44,100, 88,200, 176,400 Hz;
- For DVDs: 48,000, 96,000, 192,000 Hz.
Changing the sample rate might lower the quality a bit. But the top sample rate converter should keep the sound as good as possible. Ideally, you shouldn't notice any loss.
Learn more about how changing the sample rate affects sound quality...
Back to top
How to Convert the Sample Rate of WAV, FLAC, DSD?
To change the sample rate:
- Open the sample rate converter software AuI ConverteR 48x44.
- Load an audio file via Open files button.
- In the main window, under the Format section, select the desired audio format.
- Choose the new sample rate.
- Pick the bit depth value.
- If you set the bit depth to 16 bit, turn dither ON. (For 24 bit or higher, dither setting doesn't matter)
- Select a folder for the converted files (see the video or read the guide).
- Press the Start button.
- Wait for the conversion to finish.
Note: The free version has some restrictions.
Back to top
How to work sample rate converter
The algorithm for sampling frequency change consists of following steps:
1) Increase up of sampling rate (oversampling) to frequency, multiply target signal's sampling frequency.
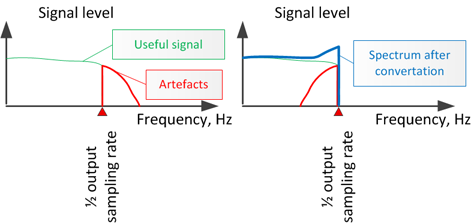
2) Filtration of "parasitic" signals (named "artifacts") above half of the target frequency of digitization.
3) Make multiple decimation of superfluous samples for decreasing sampling rate (downsampling).
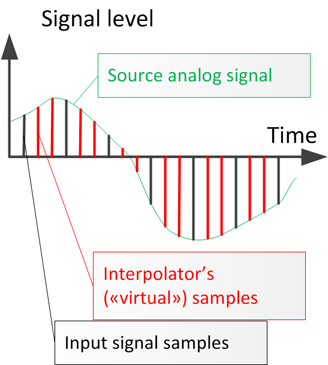
An increase of sample frequency is made by way of inserting additional ("virtual") samples between "real" samples of input digital signal. These "virtual" samples are generated by the interpolator.
The insertion of "virtual" samples, containing zero-level values, may be applied. It is a faster method for calculations than spline function, in instance. The last oversampling way adds a significant amount of "artifacts".
Why it is necessary to increase frequency of digitization? It's needed to execute goal 3) of the algorithm. Sample decimation is most easier when it is multiple: just delete superfluous.
Further "parasitic" signals, with frequencies above half of target sampling rate, are filtered. Otherwise, after deleting "superfluous" samples, "artifacts" will added to the spectrum of an audible signal. They will distort it, or add noise. "Bad" sound will happen.
Back to topDoes sample rate conversion affect sound quality?
For reduction of distortions, added to converted signal, we should interpolate it as much as possible precisely. Interpolation accuracy is closest coincidence of initial analog signal with interpolator's "virtual" samples. It is necessary to remember, that the top-quality interpolator can restore an initial analog signal precisely enough. But not with 100 % accuracy. Alas. At increase of sampling frequency there will be "parasitic" signals above half of output signal's frequency of digitization.
During development of hi-end sampling rate converters, special attention is paid to quality of low frequencies filter. If this filter will not suppress "artifacts", it will mixed with useful signal after deleting of "superfluous" samples.
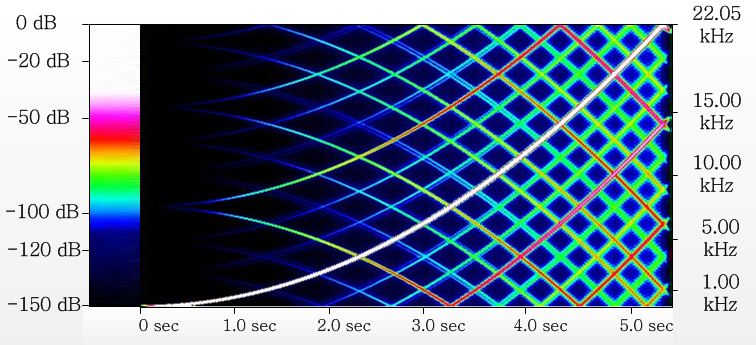
For demonstration of filtration's quality we shall look at the time-diagram of spectrum. Horizontal axis there is time, vertical axis - frequency. Vertical lines - is spectrum into time point at horizontal axis. The level of signal is shown by color (white - the highest, black - the lowest - less minus 150 dB). Sinusoidal audio signal with sweep frequency (height of tone) come to input of sample rate converter.
Spectrum analyzis
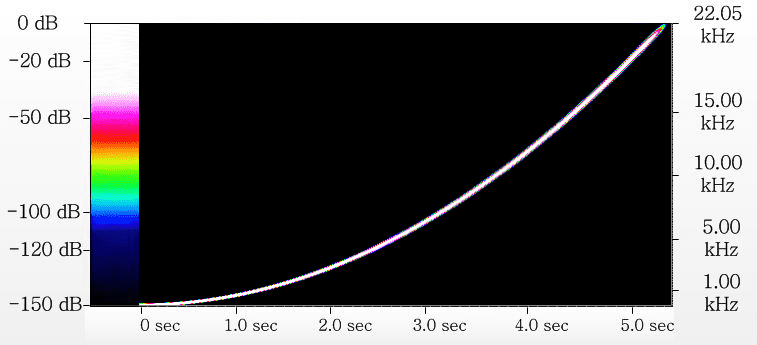
Here such result will be on an output of hi-end audio converter:
We see only recurrence of input signal, without in addition appearing frequency components - "artifacts". Level of artifacts less minus 150 dB. Less quantizations error level for 24-bit samples (minus 144 dB). Inevitable loose quantizations errors will mask "artifacts".
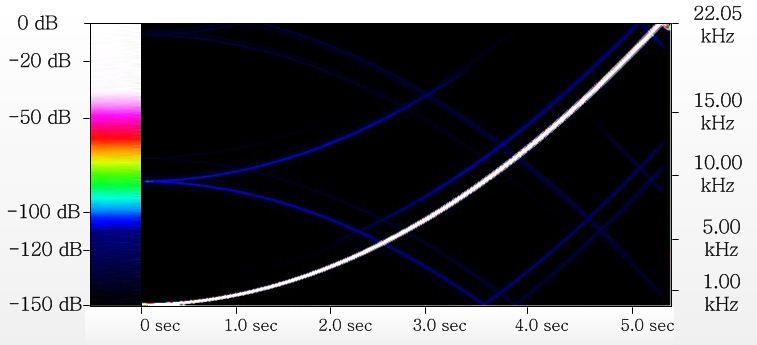
The high and middle quality audio converter of sampling frequency will give a following picture:
Here shown "artifacts" having a level near minus 105-110 dB (dark blue color) . These "artifacts" arise, both at interpolation, and at insufficient suppression (before decreasing sampling rate) of the "parasitic" signals located above half of frequency of digitization.
Let's look for comparison the spectral diagram of too low quality converter:
In this case "artifacts" achieve a level near minus 50 … 60 dB (red and pink colors).
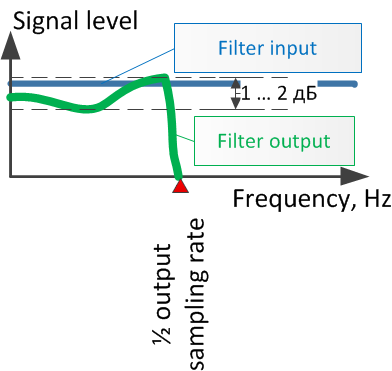
Reasmpling filter
The filter should pass audio a signal at different frequencies from 0 up to 20000 Hz without changing loudness useful. For this purpose inflating of the frequency characteristic (on different frequencies at passage through the filter) should not exceed change of a level of loudness of output signal less 1 … 2 dB.
As much as possible to keep waveform of transformed audio signal it is required to provide an identical time delay for all spectral components at passage through the filter. It is provided, if the filter have linear phase-frequency characteristic. Linear is means in the form of a flat inclined line.
At such form of the phase characteristic all spectral components have an identical delay. The signal passes through the filter not deformed{distorted}. It is especially important for maintenance of quality sounds with sharp attack (drums, piano, guitar, etc.).
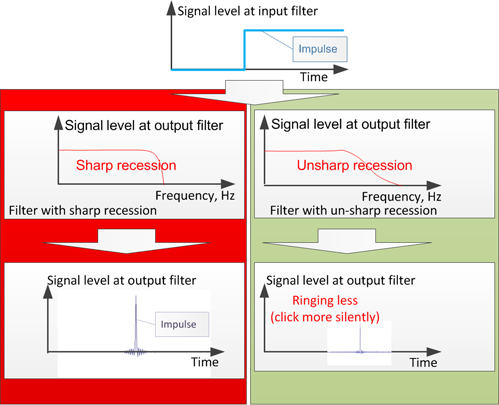
Besides filters have such feature, as "ringing". It parasitic filter's output self-oscillation by sharply changing of input signal. Apply impulse to input of converter. At output the impulse turns to the oscillation stretched on time. "Ringing" is heard as click.
The more "sharp" recession to a level between pass bands and suppression band of filter, the more level of "ringing".
Therefore it is necessary for developer of the converter to choose the compromise between a sharpness of recession of filter's amplitude-frequency characteristic (that in the most positive influences to suppression of "artifacts") and level of "ringing". Very heavy case, when final result of conversion is sample rate 44,1 kHz. Between the maximal frequency of a useful signal (20 kHz) and half of frequency of digitization (22,05 kHz) the difference on frequency makes only 2,05 kHz. At a desirable degree of suppression of artifacts nearby 140 dB!!!
Conclusions
Quality of sampling rate conversion depends at:
- quality of interpolation;
- value of oversampling frequency;
- quality of filtration before decreasing of sampling rate.
For the majority of modern records 24-bit samples is used. It achieve theoretical level of quantizations noise minus 144 dB. Accordingly the level of all transformation's "artifacts" should not exceed minus 144 dB. Thus "artifacts" will masked in noise of quantizations. There is no reasons make level of "artifacts" less noise of quantizations.
Quality of converting signal is provided with filter's linearity phase and evenness of frequency response.
See description high precision sample rate converter AuI ConverteR 48x44.
Back to top
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you convert sample rate?
You can convert sample rate according to the manual...
Is 44.1 kHz a good sample rate?
Sampling rate 44.1 kHz is minimum discretization frequency to transmit audible range. Minimum frequency causes additional issues for developers of audio equipment and software.
Read more...
Can I change the sample rate from 44.1 to 48?
You can change sample rate from 44.1 to 48 kHz according to the guide...
- Oversampling >
- Downsampling >
- Multiple vs. Non-Multiple Resampling Audio >
- Would need sample rates 352 and 384 kHz >
- About reasons of using optimal sample rate (pdf).
- Samplerate converter comparison
Back to top