Audio Basis - articles about audio
Oversampling (upsampling) is sample rate multiplication. As rule, oversampling is meant a multiple increase in sampling frequency. There is an opinion, that non-multiple increase in sampling rate causes sound degrading. Read how oversampling works and what sound advantages or disadvantages there are.

If you buy "AuI ConverteR PROduce-RD" (2023/12.x version) from 24 August 2023 to 24 October 2023, you will get free update to version 2024 (13.x) after its release.

Why would you upsample?
As rule, you have multiple musical devices: players, DAC, etc. These devices support different audio resolutions.
And, you are required to adjust the audio file resolution to these devices.
In instance, you can optimize audio file resolution to DAC's sound quality abilities.
Back to top
Upsampling
A digital signal is a sequence of signal values. The values are situated in equal time periods from each other.
When we play the sequence back, a loudspeaker produces oscillations (sound). In the first approach, each value is an air pressure to an eardrum in the current moment.
Interpolation is a method, that can find "virtual" values between real values. Virtual value is calculated by available real values.
Interpolation allows non-multiple altering of the sampling rate. The method has non-linear distortion issues. They are defined by method type, the number of real values, etc.
Alternatively, a non-multiple rate may be done via multiple oversampling and decimation of the sampling rate.
In instance, 44.1 to 48 kHz may be done as 44.1 kHz x 160 / 147 = 48 kHz.
And, 48 kHz x 147 / 160 = 44.1 kHz.
Back to top
Oversampling vs upsampling
Any digital signal has a sample rate that defines its spectrum (low, high frequencies of a sound, in instance).
Upsampling is an increasing sampling rate on multiple or non-multiple ratios.
Oversampling is a multiple-ratio upsampling.
Though, these terms have no exact definition.
Upsampling may be done via interpolation (spline math function, as example).
But, multiple upsampling (oversampling) may be done by inserting zero samples. And, it may cause lesser non-linear distortions in proper applications than the interpolation.
On the other hand, non-multiple upsampling may be done via multiplication and dividing to integer ratio.
You can read the details below.
Back to top
Oversampling
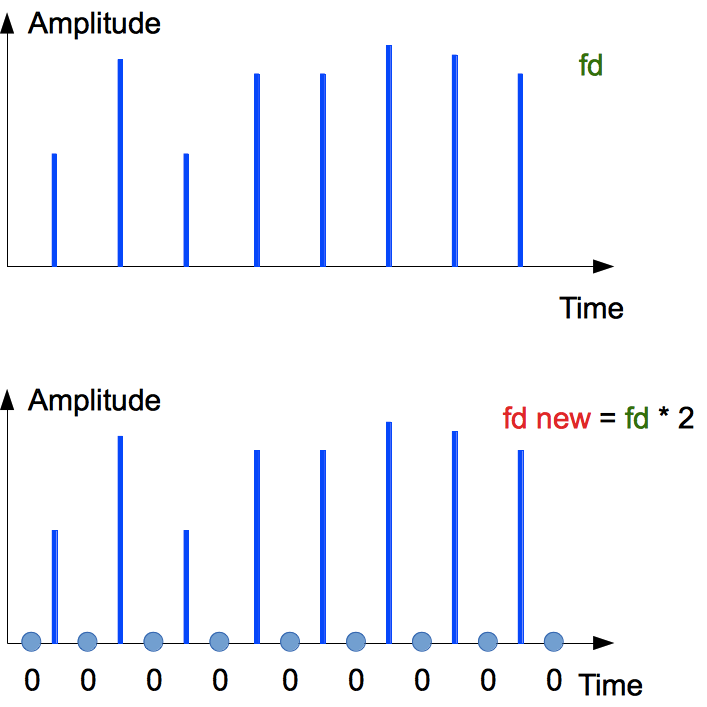
Usually multiplexing of sample rate is released as inserting ZERO SAMPLES (virtual samples) between "real" source samples.
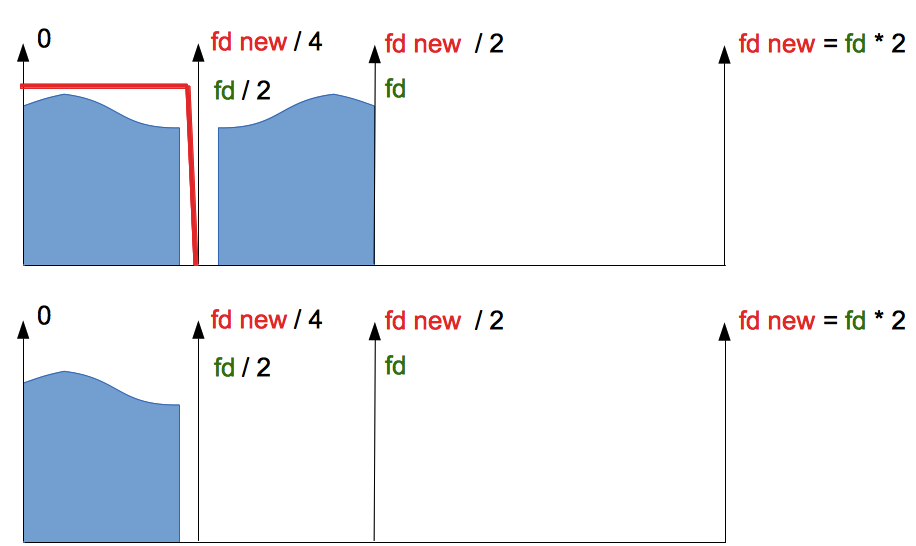
After oversampling, the spectrum is mirrored and flipped to the upper half of the old sample rate fd. So we get mirrored copy of the source audio spectrum (upper part of the picture).
Resampling filters
It is non-linear distortions in output (oversampled) audio signal.
For getting a non-distorted (almost non-distorted, of course) and oversampled audio signal after oversampling, it needs to apply low-frequency filtration with the band from 0 to fd/2.
Back to top
Sound quality
Sound quality of oversampling or upsampling is defined by resampling filters.
In ideal case, all mirrored audio content should be suppressed, but audio content below [input sampling rate]/2 should be removed.
But there are no ideal resampling filters. And unwanted mirrored audio content folded to the audible range and causes distortions.
Also, digital filters cause ringing and frequency distortions.
However, the author doesn't know about serious studies, that prove actual ringing harm. And frequency distortions may be reduced significantly below human perceptions.
Digital filters have several contradictory features. And filter design is a balance of the parameters, which is an art of development.
So, with proper resampling filters, we get an almost clean oversampled source audio signal (music).
Read more:
Back to topHow to upsample audio
To upsample audio:
- Start audio converter software AuI ConverteR 48x44.
- In the main window, click Open files button and select source audio DSD and/or PCM files.
- In the right of the main window > at Format panel, select target audio format (WAV, FLAC, etc.), sample rate, bit depth.
- Select target directory for converted files
In the main window (left lower part) > Directory output files field.
Read more...
- Push Start button.
- Wait for conversion end. Converted files are placed into the directory assigned in goal 4.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is upsampling audio good?
It's important to remember, that upsampling is an information lossy process. However, proper resampling has minimum losses, as rule, below human perception.
On the other hand, we can optimize your music file's resolution to use DAC to reduce playback distortions. Read more...
What is upsampling audio?
Upsampling is a increase the sampling rate of digital signal. Read more...
Is upsampling same as oversampling?
Upsampling is a multiplication of sampling rate. Oversampling is an integer multiplication.
Read more...
Does upsampling degrade audio?
Upsampling causes losses of information because a resampling filter is used. However, high-quality filters cause extremely low distortions. And it may not be considered.
For audio, music-file upsampling may be used as a way to reduce DAC distortions. Read more...
Does DAC upsampling?
DAC receives a range of sampling rates. Most popular DAC schemes use sigma-delta modulation (like DSD) with oversampling at the final stage for better analog filtering.
There are also DACs that are non-oversampling.
Read details...
What is audio upscaling?
The author knows nothing about "audio upscaling". Probably, it's "upsampling" or "oversampling".
Read more...
- Audio Sample Rate Converter >
- Downsampling >
- What Better Multiple or Non-Multiple Resampling >
- Would need sample rates 352 and 384 kHz >