When we look for a home theater, buy and install AV receiver and TV, digital audio players, DACs, we read equipment manuals and discussions. In this article, the author will explain: what is LPCM amd PCM audio, bitstream audio, PCM vs Dolby Digital, DTS, DSD, TrueHD, mp3, WAV, lossless, and many others. Keep reading.

If you buy "AuI ConverteR PROduce-RD" (2023/12.x version) from 24 August 2023 to 24 October 2023, you will get free update to version 2024 (13.x) after its release.

Back to top
Overview
As rule, TV equipment suggest us choose between auidio formats: PCM and Dolby Digital, or PCM an AC3.
In simple words, the author can give recommendations for SPDIF audio connection:
If you use stereo audio only no more than 16 bit / 48 kHz, select PCM for the best sound quality.
If you also listen multichannel audio or stereo above 16 bit / 48 kHz, select Dolby Digital or AC3 (original name of Dolby Digital).
If you use HDMI connection on new equipment, use PCM audio.
Read details below.
Back to top
What is PCM audio
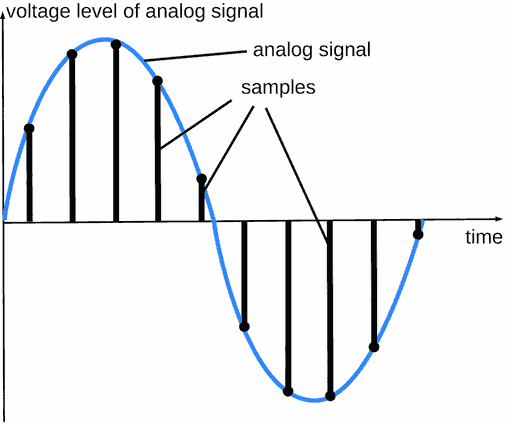
PCM audio (Pulse-Code Modulation) is one type of digital audio. An analog electrical signal from a microphone is converted to digital form. In AV-applications PCM is a data-uncompressed alternative to Dolby Digital technology. PCM is representation of an analog acoustic waveform as sequence of samples. They keep sound oscillation states in time.
In simple words: What does PCM audio do?
Audible sound is air oscillation ("music"). It's continuous. Microphone converts these oscillations to electrical ones (analog audio).
PCM audio takes instant values of the electrical oscillation and saves it as a number sequence.
The value (number) is called the "sample".
Digital vs Analog:
Analog signal is continuous. Digital signal is discrete: consists of samples (discrete pieces).
Example:
Analog signal is like water. Digital signal is like multiple boxes with water. These boxes have infinite thin walls.
See details below...
For home television equipment, PCM or LPCM is a digital audio format that is transmitted from TV to AV receiver, in instance. The format should have no quality losses (lossless).
Such PCM bitstream has no size compression. And audio data in some high resolutions may not be sent via a connection interface (SPDIF, in instance).
The channel number is limited by allowable throughput too.
To use PCM/LPCM for high-resolution audio (especially, multichannel), HDMI interface is recommended.
- A computer can't store continuous thing like an analog audio signal. So, the signal should be represented as discrete values (samples), that may be stored in the computer memory.
- Before listening, these discrete values should be transformed back to a continuous signal. And here we have many myths.
- The main advantage of discrete values is the ability to transmit/store with control of errors and technical opportunity to recover it (when special coding is applied). From a design point of view, digital audio technologies allow for achieving lower distortions, than analog ones.
Read:
Back to top
What is the difference between Pulse-Code Modulation and Dolby Digital?
In audio and video (AV) equiment, we face Pulse-Code Modulation and Dolby Digital. Both these terms means technologies or interfaces for audio-data transmitting between AV-units: TV, AV receiver, etc.
Physical audio interfaces that connect these units has data throughput limitation.
PCM is lossless audio stream that brings maximum sound quality. But Pulse-Code Modulation causes high bitrate and requires significant throughput abilities. Channel number increases data stream bitrate too.
Dolby Digital is data compressing technology. It's family of formats. Dolby Digital allows reducing the stream value. Especially for multchannel audio, it gives abilities to convey:
- stream with lesser data-compression level for better sound quality;
- higher sampling rates, bit depths.
Dolby Digital allows lossy and lossless data compressing. Lossless compressing consumes more throughput but has better audio quality.
For lossy formats of Dolby Digital family, higher bitrate should bring better sound quality.
Read more about Dolby Digital...
Back to top
PCM audio formats
Most digital PCM audio formats (
and other) contains musical signal in this PCM format.
Audio data may be size compressed to solve the issue of:
- medium capacity or
- throughput limitation of communication channels (or audio interfaces).
Compression may be lossless or cause sound quality losses. Read details...
Sometimes, data-compressed audio is called a bitstream. Read more...
Audio interface is hardware device to:
- convert analog to digital signal and/or back;
- transmit audio (in digital or analog form between devices).
Audio interface is part of computer, AV-receiver, TV, DAC, DAP (digital audio player) and others.
DAC is a digital-to-analog converter. It's a kind of audio interface.
Audio output is a connector, audio data transmission protocol and hardware, including an audio interface, to transmit audio data to another device. Audio output may transmit signals in analog form. It's analog audio output.
Bitstream is a throughput volume in bit per second (kbit per second, kbps).
Lossless is a compression or storage audio without sound quality losses.
Lossy is compression or storage audio with the losses.
Audio file is a computer file that contains audio (including musical) information.
Back to top
How PCM works
Back to topBrief overview
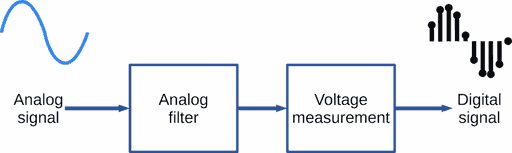
Audio signal in a musical system (amplifier, AV receiver, etc.) is altering voltage like acoustical waveform changing.
Special device - analog-to-digital converter - rapidly measures momentary values of the audio signal (its voltage).
These values may be converted back to the audio signal via digital-to-analog converter device.
PCM audio in simple words
Sound is a wave in a sea.
The wave level is up and down, up and down...
Level of the wave can be measured by a ruler.
We can measure the level 10 times per second and sequentially write these values.
Let's imagine a machine, that can form the water level by the written value sequence. And we get the same water wave.
Read details below.
Back to top
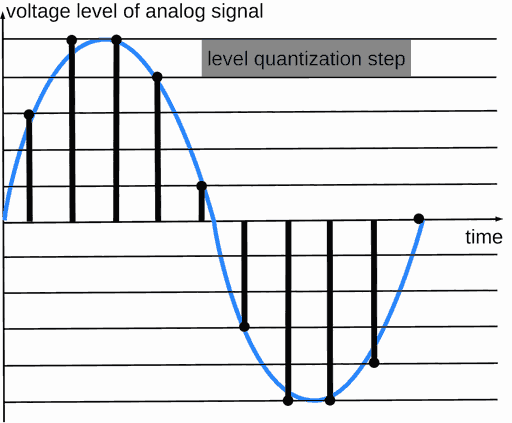
PCM analog-digital converter, quantization
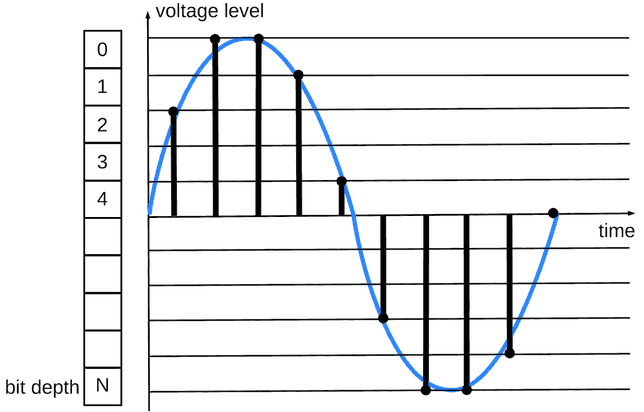
Analog-digital converter (ADC) is a device, that periodically measures analog signal voltage and sends the measured values as numbers (in digital form) to PCM digital audio output.
PCM encoding is the conversion of an analog signal to digital form.
The period between measurements is the same.
Sample is a digital value of measurement (amplitude).
Quantization is the measurement step of the voltage level of an analog signal.
Maximum amplitude in digital form has 0 dBFS value. dBFS is decibel in relative full scale, 2Nbit.
Samples may be stored and transmitted without altering information. It is the main advantage of digital signals, comparing analog ones.
However, binary data may be damaged during storing and/or transmission.
Back to top
Sample rate
Sample rate (sampling rate) is a number of samples per second (measured in Hz, Hertz).
The sampling rate is constant for audio stream that is coded via pulse-code modulation.
As rule, an analog signal is coded as real numbers (math definition), which are usual numbers we use permanently.

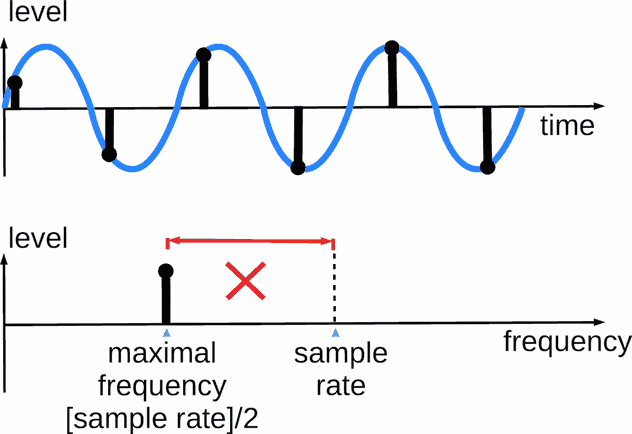
Nyquist theorem
Nyquist theorem defines a theoretical minimal sample rate.
Let's pay attention to "theoretical" word. Real implementations require to account other factors too. Read below about myths, where we'll discuss, why higher sample rates are used.
In simple words (it is not an exact math definition) the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem may sound as:
One of popular myths is "sample rate / 2 is enough".
A coded digital audio signal has a total band=[sample rate]/2
Below we will consider the theorem details, when 44.1 kHz / 16-bit sound quality matter is discussed.
More exactly the theorem wording in technical terms:
Endless analog sine signal may be coded (to digital form) and restored with sampling rate 2 times more than the signal's frequency.
"Endless" is keyword here. But real musical signal components are finite.
More samples per finite signal duration keep more information about source signal to restore it from digital to analog form.
More samples per signal duration is closer to infinitive sample rate.
But, the most important issue is unperfect analog filter, which is used as an interpolator in DAC and as alias (distortion) remover in ADC. Read below how it works.
Alternatively, the input samples may be processed via Hilbert transform. It converts real numbers to complex ones.
The complex number contains real and imaginary parts.
In this case, a coded digital audio signal has a total band=[sampling rate].
However, it has no big sense in audio, because digital data size is the same.
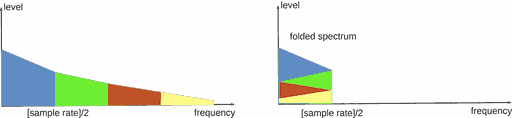
Analog-digital converter capture full frequency band at the input. But all stuff above [sample rate]/2 is folded with band {0 ... [sample rate]/2}. It adds noise to the coded digital signal.
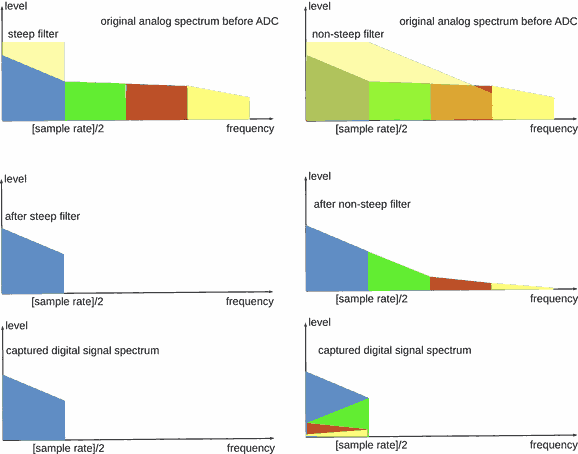
Thus analog signal band above [sample rate]/2 should be cut.
But the analog filter isn't steep enough. The issue is solved via a higher sampling rate: higher sample rate is lower filter gain at [sample rate]/2 point (lesser signal at the filter output).
To increase steepness, a digital filter is used. But it adds additional distortions.
Also in DAC sampling rate may be increased (oversampling) to better work with the analog filter. Oversampling works with the digital filter in pair.
There is a myth that non-multiple resampling causes more distortions, than multiple one. But in case 48000 and 44100 Hz, resampling is applied the same way.
Read more about sample rate conversion (multiple vs non-multiple) >
Back to top
Bit depth
Bit depth is number bits of number code (word), that store analog signal value.
Bit depth defines the number of digital levels, that can be stored.
Maximum value of the word is the maximal positive value of an analog signal at ADC input. Its code is:
Vmax=2(N-1)-1,
where N - number bits of the word.
Minimal value of the word is maximal negative value of the analog signal at ADC input. Its code is:
Vmin=-2(N-1).
The total number of measured levels is:
L=2N.
Bit depth truncation is bit depth reducing via removing of one or more bits.
Rounding is bit depth reducing via removing of one or more bits with altering of reduced number according to removed bit(s).
Rounding may be applied when float point bit depth is converted to integer one.
Rounding is more exact mathematically, than the truncation.
Back to top
Quantization noise
Codes of analog values, stored into the words have precision limitation. The limitation is defined by total number of measured levels L. So stored codes (samples) are not equal exactly to real analog voltage.
Quantization error is difference between sample (digital value) and real voltage of analog signal.
The error is various for each sample and lesser than 1.
The error is observed as quantization noise at digital signal spectrum.
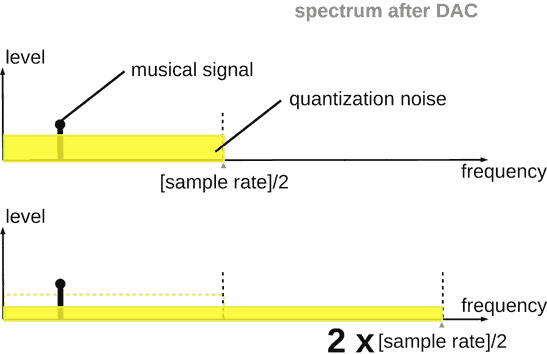
The quantization noise is equitably distributed across frequency on the digital signal spectrum.
The energy of quantization noise is constant in total band. Thus, increasing of the total band of an analog signal after DAC (sampling rate increasing) decrease the noise level in the audible range [0 ... 20 kHz]. It happens because audible range has a fixed width.
depends on the band of an analog signal
Of course, real DAC has output electrical noise. As rule, its level is about -117 ... -120 dB.
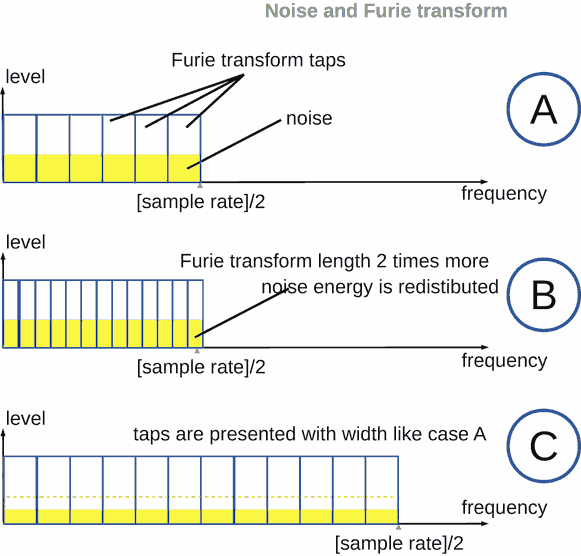
Quantization noise altering for bit depth and sample rate
| Pa |
Quan |
Do |
| [sample rate] x 2 | -6 dB | in analog domain |
| [bit depth] x 2 | -6 dB | in digital and analog domain |
| [Fourier transform length] x 2 | -6 dB | in digital domain |
In the digital domain quantization noise level is decreased about 6 dB for Fourier transform length 2 times more.
Quantization noise level formula for bit depth M:
NQ=1/(2M × V12) [11], where
V12 is the square root of 12.
In the digital domain, NQ is the same independently sample rate. But the Fourier transform divide digital band to parts (small sub-bands). Number of the parts is [the transform length]/2 (for real samples) and [the transform length] (for complex samples). I.e. more the length, more the parts, lesser energy into each of the parts.
Fourier transform is converting oscillogram (time domain) to spectrum (frequency domain).
In digital audio, we mean discrete Fourier transform in most cases. The discrete mean, that spectrum is divided to taps.
Fourier transform length is tap number.
FFT (fast Fourier transform) is case of Fourier transform. It's length is 2K, where K is integer number.
If there are tips 2 times more, noise energy is redistributed. And each tap have energy 2 times lesser.
Noise energy is square of noise part, concluded into tap.
If we make tap width as before the redistributing (tap width at the part A of the picture), noise level will 2 times lesser. Because square of noise is constant. It happens on computer display, when tap width have same pixel width on a screen.
Read below more about bit depth, quantization noise and dynamic range for 16 bit implementations.
Back to top
PCM digital-analog converter
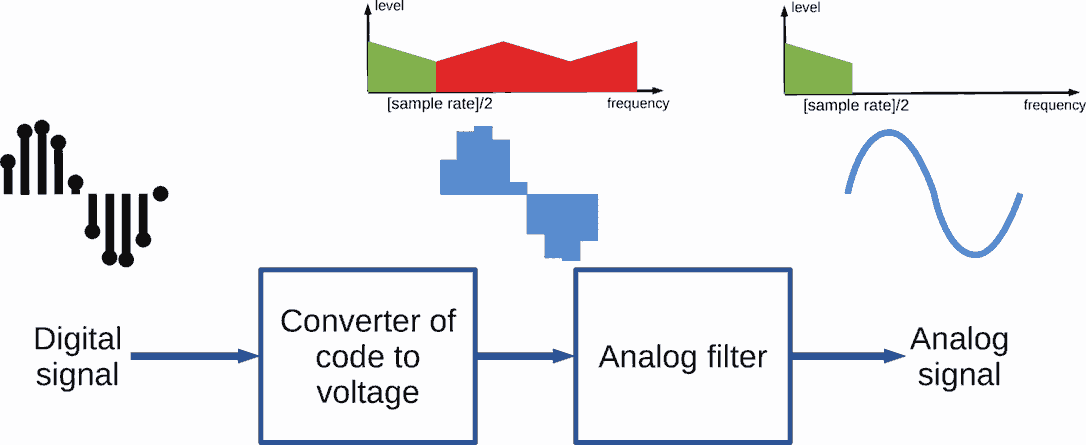
Digital to analog converter transform samples to analog values.
PCM DAC demodulation:
- convert digital codes (samples) to voltage levels,
- filtering aliases via output filter.
At first glance, PCM DAC produce "stairs" at output. But it is not so. Because "the stairs" are smoothed by analog filter at the digital-analog converter output.
It allow to says, that analog signal in band 0 ... [sampling rate]/2 is fully restored.
But that's not exactly true. Because the analog filter isn't ideally "brick wall".
Non-filtered "stair" spectrum contains:
- useful musical signal at bottom of the frequency axis;
- aliases, that is copies of the musical signal. They are repeated along frequency axis.
Half of the aliases are flipped horizontally. In ideal audio system without non-linear distortions these aliases will inaudible.
But:
- in real musical systems non-linear distortions can cause intermodulations, that generate audible products by inaudible components.
- aliases consume part of dynamic range and reduce dynamic range abilities of the useful musical signal.
Both of these issues are solved via "stair" filtering.
Read more how to works DACs, about its advantages and disadvantages:
Back to top
PCM file formats (pcm audio codecs)
Codec is hardware or software of:
- encoder (encode PCM to an audio format);
- decoder (decode an audio format to PCM).
In the table noted only file abilities, that author know. If you have additional information to correct description or other, contact us.
PCM file types
| Type | Loss |
Los |
Hi-Res ca |
Mul |
Me |
Ad |
| WAV | yes | yes | yes | yes | text meta non-standard artwork imp |
SONY WAV64 and WAV RF64 formats have big file (more 2GB) ability |
| FLAC | yes | flac file as con |
maximal resolution 32 bit 384 kHz | yes | sup |
Ca |
| AIFF | yes | yes | yes | yes | Text meta non-stan |
|
| ALAC [4] | yes | yes, maxi |
up to 7.1 | sup |
||
| CAF | yes | yes | yes | yes | May be re |
Big file (more 2GB) ability |
| mp3 [5] | yes | no (32, 44.1, 48 kHz only) | stereo only | supported | No size li |
|
| MQA [3] | yes | yes | supported as FLAC (when FLAC con |
May be: - pro - play |
||
| AAC [6] | yes | yes, up to 96 kHz | up to 5 channels | supported | De |
|
| DTS [8] | yes | yes | up to 24 bit / 48 kHz (core) | 5.1 | de |
Dol |
| Dolby True |
yes | up to 24 bit / 192 kHz | up to 8 chan |
Dolby Di |
||
| ac3 [9] | yes | no (up to 48 kHz) | sup |
depend on con |
||
| WMA [10] | yes | yes | yes, up to 24 bit / 96 kHz | sup |
sup |
Comments to the table:
"bit" mean bit-depth value (example: 24 bit),
"kHz" mean sampling rate value (example: 96 kHz).
Sometimes files with same extension may contains different extensions. Examples: *.m4a files can contains either ALAC or AAC; FLAC can contains either FLAC or MQA or DoP.
A reading software (player, converter, editor, other) parse file. As rule, file consists of data blocks. These blocks have identifiers. And the reading software recognize the block types. Sometimes the software check data integrity. If there are non-correct data, the software may to reject file opening (depend on implementation).
Size compressed file types are used for saving hard disk space. Especially, it is actually for portable devices: digital audio players (DAP), mobile phones, etc.
"Big" home audio systems have no disk space issues in many cases.
Portable devices are able to playback multichannel files. But it is listened at stereo headphones, as rule. So multichannel records consume disk space to extra channels. The space extra size issue may be solving via downmixing audio files to stereo.
Downmixing quality depend on implementation.
Read below about PCM sound quality issues
Back to top
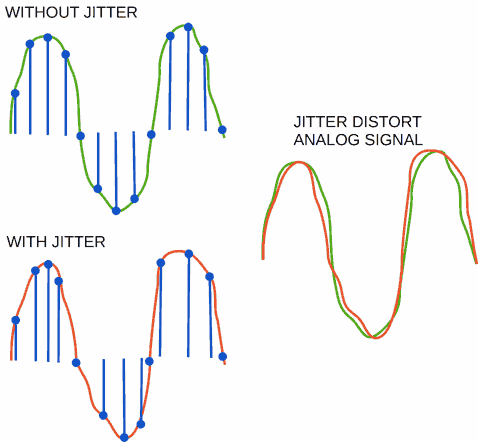
Jitter
Jitter is unstability periods of samples. It cause non-linear distortions/noise.
Jitter appear in ADC and DAC. It is impossibly to get rid of jitter in real music systems. Because there are electromagnetic interference, non-stability of clock generators, power line interference issues.
However, the jitter may be minimized via special technical decisions.
Read more about jitter >
Back to top
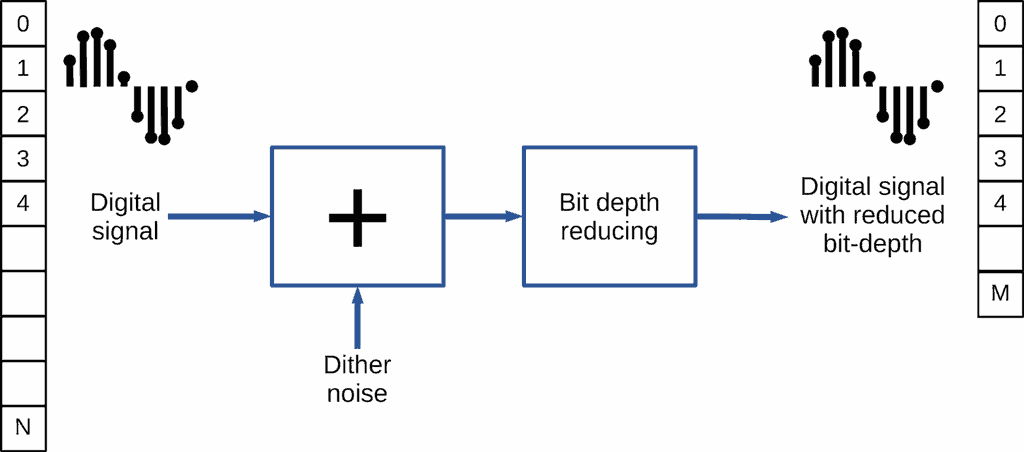
Dither
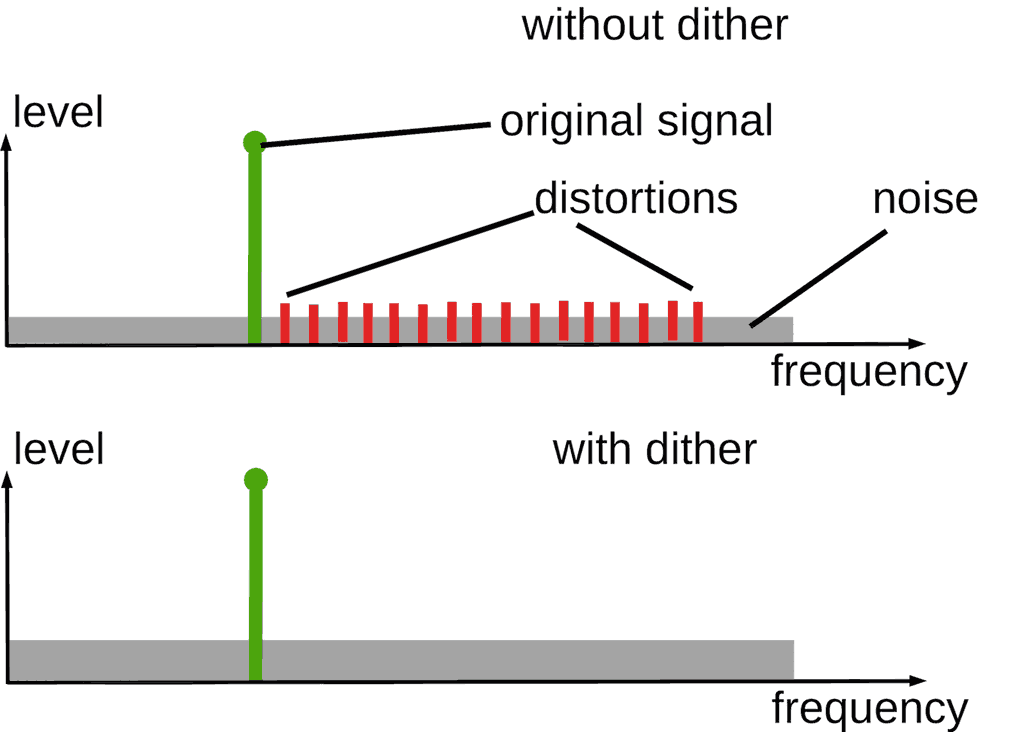
Quantization error cause non-linear distortions. It correlate with musical signal. Correlated distortions are considered as especially unwanted to perceived sound quality.
To decorrelate the distortions and the signal, dither is applied.
Dither is extremely low level noise, that added to musical signal before ADC or before bit depth truncation prior to DAC.
To reduce noise in audible band, noise shaping may be applied. It looks like "pushing" of noise energy to upper part of frequency range. But the shaping demands of band reserve to the "pushing".
Read more about dither >
Back to top
PCM data compression
Data size compression of audio content is way to save space at hard disk or increase throughput in communication line. Compression is performed by encoder and decoder software.
There are 2 types of the compression: lossless and lossy.
If audio data content isn't compressed, it lossless always.
Back to top
Lossless
Lossless compression is size compression when input and output binary audio data content are identical.
Lossless PCM formats: WAV, FLAC, AIFF, ALAC, APE, ...
Lossless formats have same sound quality. There is opinion, that different sound may be there. Some objective hypotheses exists too. But still no researches, that are famous to author.
Also DSD may be packed in PCM as DoP audio format.
Read more about lossless audio...
Back to top
Lossy
Lossless compression is size compression when input and output binary audio data content aren't identical.
Lossy PCM formats: mp3, AAC, DTS, MQA[3], ogg, ...
Lossy formats have different sound losses.
We can compare lossless and lossy formats technically.
Different lossy formats look for minimal losses by psychoacoustic criteria. And these compression methods are based on various hypotheses.
As example, AAC format was developed to improve mp3 sound quality according newer knowledges about brain processing of sonic information [1].
Back to top
Alternative format comparison
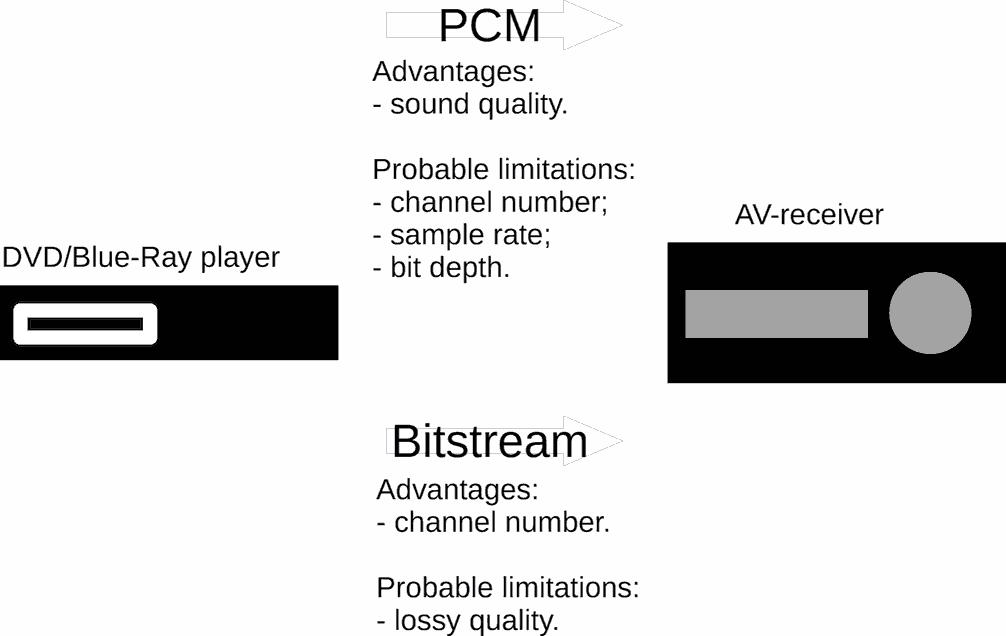
Back to topPCM vs Bitstream
"Bitstream" is non-official name of compressed by size lossy/lossless coded streams (PCM, Dolby, DTS, etc.). I.e. it is streams that have stream volume (bit/sec) feature as compression estimation. As example, PCM vs Dolby Digital is one of cases of PCM vs Bitstream. From this point of view, mp3 and FLAC are "bitstream" too.
As rule, higher stream volume for single codec give better sound quality. But, other hand, higher bitrate may lead to lesser channel number in fixed band width of digital interface. As example, stereo instead multichannel.
AV users asks what is use PCM or bitstream to transmit data from player to audio-video receiver of home theater.
If your player and AV-receiver are capable to PCM (including multichannel [if it is need]), then use PCM. Otherwise, use bitstream codecs.
As rule, bitstream is recommended for SPDIF interface. HDMI (latest versions) can transmit multichannel PCM (LPCM).
Back to top
PCM vs Dolby
Dolby is size compressed PCM. It used to transmit audio signal thru digital audio interfaces with lower speed. As example, multichannel audio thru SPDIF.
If compression is lossless, it is not matter Dolby or original PCM there. Lossy compressing cause some quality losses.
Generally, it is impossible to say, the losses will audible or not.
Back to top
PCM vs DSD
It is impossible to compare PCM and DSD from technical point of view. Because different hardware is used there.
Sound quality don't depend on format. But audio quality depend on format implementation.
DSD after edition demands re-modulation. PCM don't.
DSD DAC is simpler than PCM digital-analog converter.
Read articles:

Back to top
WAV vs FLAC
WAV and FLAC is binary identical. They both provide the same sound quality.
Read details here >
Back to top
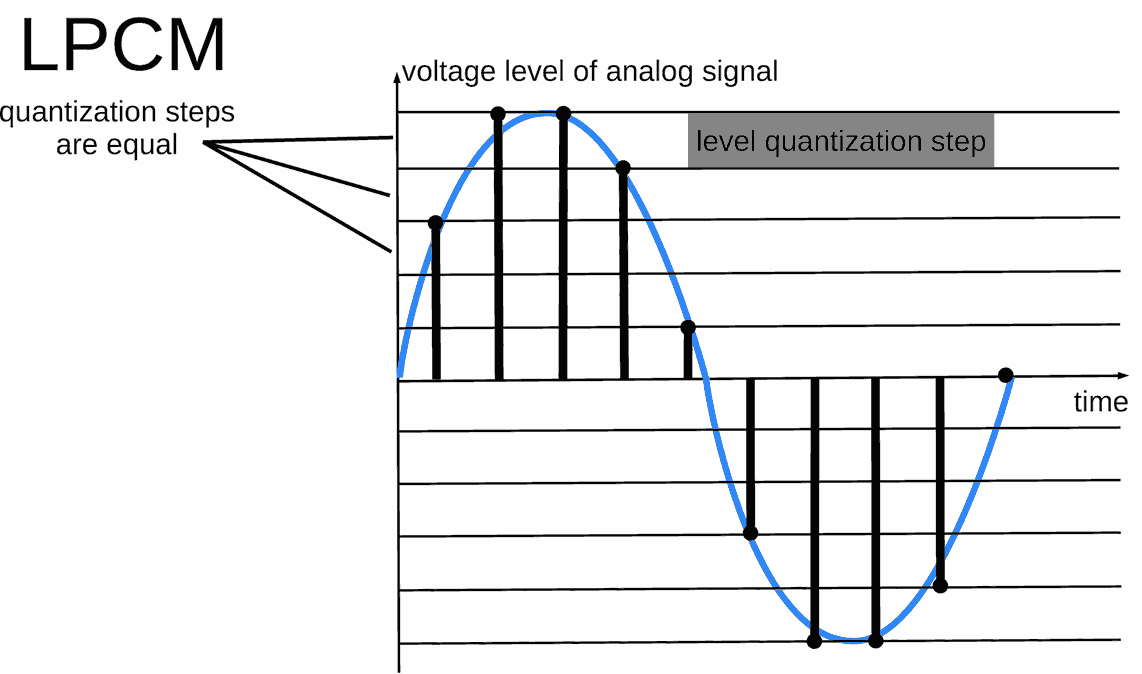
LPCM
LPCM (Linear Pulse Code Modulated Audio) is PCM with regular intervals between quantization levels of analog voltage. It is common PCM in audio. [2]
Sound quality
Sound quality mean distortion level. However, distortions may have different distribution by frequency and phase. And distortions must be estimated in the light of psychoacoustics.
Back to topWhat is the best sample rate
Aliases (distortion) appear during analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog conversion. Sample rate define the alias period on frequency axis. The period is half of sampling rate. All audio content above the period should be removed to avoid of distortions of useful musical signal.
The analog filter makes the removing. However, analog filter isn't steep. So, the higher the [sample rate]/2 the deeper suppression.
Higher sampling rate help to implement ADC and DAC with lesser distortions.
Back to topWhat is the best bit depth
Bit depth define minimal noise level into record. The bith depth should provide noise level below noise floor of electrical circuits of ADC and DAC.
If recorded musical stuff will digitally processed (gain increasing, equalization, level normalizing, other), noise floor of processed stuff should be below DAC noise level.
In audio software, processing may be implemented in 32- or 64-bit float point formats. These formats have high precision (low quantization noise) and better overload abilities, than integer ones.
As far as author know, DAC can't receive data in float point formats. These formats are rounded to integer into playback software to send to DAC.
DAC with sigma delta modulator are able to receive float point formats. But author know nothing about such real implementations.
So, need to consider necessity in noise floor reserve to take of bit depth value.
Back to top
What about 16 bit 44100 Hz? Myth reasons
Author consider as myths two states:
- 16 bit 44.1 kHz is enough because we can't hear ultrasound,
- High resolution (above 16 bit 44100 Hz) give more sound details.
Below author try to explain why he think so.
Nyquist theorem is well known. We know and can easy practically check 20 000 Hz audible limit.
It give base to myth that 44100 Hz is maximally reasonable sample rate. Because in 2 times more 20 kHz plus range for transient band of ADC and DAC filters. And there is opinion, that higher sampling rates aimed for ultrasound playback, that we can't hear.
Nyquist theorem, indeed, says that analog sine may be coded to digital PCM and restored back to analog without loses.
But it is ideal concept, that require infinite time of recording and playback and ideal brickwall filter.
We have no infinite time.
We have no brickwal filter actually. We have filter with some transient band.
Narrow transient band is difficult for analog filter. Steeper digital filter, more intensive its ringing distortions. Also may be technical resource limitations to build steep enough filter.
Inside DAC upsampling with digital filter is used for proper filter work. But hardware may have calculation resource limitation to implement sophisticated filter.
So high sample rates are used not for ultrasound playback, but for ADC and DAC filters.
We know that human hear sonic in range 0 ... 120 dB maximally. There is opinion that dynamic range of 16 bit is 16 * 6 dB = 96 dB.
But 96 dB is noise floor (actually it about -100 ... -110 dB).
So minimal signal -96 dB have "zero sound quality". I.e. noise cover audio signal.
To keep sound quality signal must be higher noise. We can take noise level about -40 dB as allowable.
So actual dynamic range, when sound quality is kept, is 56 dB = 96-40.
If digital signal processing is applied, total gain may be increased and noise will boosted.
We can solve low level quality issue via higher bit depth.
Back to topAudio data integrity
Digital audio data may be corrupted in transmitting or at storage. It can be checked via checksum comparison.
Checksum is unique number calculated for binary audio data array.
Checksum A is calculated for correct music data array.
Before playback, checksum B of actual data array is calculated.
If checksum A and B are different, we can suggest that the actual data is damaged.
Checksum is used for compressed data, as rule. But it may be applied for any audio file content.
Back to top
PCM software
The software process and/or playback PCM audio files, streams.
Back to topPCM audio players
- Audirvana
- foobar2000
- JRiver
- VLC
Audiophile players are capable to bit-perfect playback of audio files: audio file content is sent to DAC without altering.
Back to top
PCM audio converters
- AuI ConverteR 48x44
- JRiver
- XLD
Main demand to the converter is minimal distortions in audible band.
CD ripper is kind of audio converter that capable to copy CD audio data to file.
Back to top
PCM editors and DAWs
- Audacity
- Sound Forge
- Wavelab
Back to top
Frequently Asked Questions

What is PCM sound mode?
PCM or LPCM is mode of audio communication between TV and digital-to-analog converter or AV-receiver. PCM mode provides sound quality without quality losses.
Read more about audio transmitting modes here...
What is PCM audio format?
PCM is a digital audio format. Read about it here...
What are PCM files?
PCM files are files, that contains audio data in PCM format. Examples: .wav, .flac, .mp3, others. Read more...
What is PCM recording format?
PCM format is digital representation of recorded analog sound. Read more...
Are PCM and WAV the same?
WAV is one of PCM formats. Read more...
Back to top
F.A.Q. PCM TV
What is PCM audio on TV?
PCM is a size-uncompressed mode (format) of transmitting of an audio signal output from TV to AV-receiver or DAC. Technically, all size-compressed formats in TV and receiver are PCM (except DSD, if it's supported). PCM sound mode uses Pulse Code Modulation.
What are TV-audio modes read here...
What is PCM setting on TV?
PCM is codec type, that is used to send audio from TV to AV-receiver. This codec transmit sound data without losses of sound quality.
Read more the codecs here...
What is PCM audio setting on TV?
PCM audio settings is set of audio codec that sends uncompressed lossless PCM audio signal to DAC or audio/video-receiver.
Read details...
Does Samsung TV have audio out?
As rule, Samsung TV has several types of audio outputs:
- analog (RCA);
- SPDIF (RCA, Fiber);
- HDMI.
Most recommended output type is HDMI due to better abilities for multichannel hi-res sound streaming.
What is the best sound setting for TV?
If your TV is connected to AV receiver via HDMI, you can set PCM mode. It provides the best sound quality.
However, SPDIF inteface has limited throughput speed. So, compressed audio format may be required. Especially for mulichannel signals. Read more...
What is the best sound setting for Samsung TV?
If Samsung TV or AV-receiver is equipped with SPDIF only, Dolby Digital is recommended for multichannel audio.
Stereo audio may be limited by sample rate and/or bit depth.
If both TV or AV-receiver are equippedis HDMI, you can set PCM/LPCM mode. It provides lossless sound quality.
Read more...
When should I use PCM on my TV?
Dolby Digital is lossy formaty in many cases. However, it allows transmitting of multichannel and/or hi-res audio via SPDIF.
LPCM/PCM may be recommended for TV with HDMI output.
Read more...
Is PCM a digital signal?
Yes, PCM is one of digital signals.
Read more...
Is PCM lossless?
In AV-applications "PCM" term is lossless PCM audio.
Is PCM audio compressed?
PCM audio may be compressed or not. In audio/video, as rule, "PCM" means uncompressed audio.
Read more...
What does PCM mean?
PCM is abbreviation of Pulse Code Modulation.
What is PCM audio output?
PCM audio output is hardware interface (connector and its controller). Example: HDMI, SPDIF, Toslink. The interface is capable to transmit digital audio data in PCM format.
What is PCM and RAW?
RAW is pure audio data without meta-information about the data. The information contains: sample rate, bit depth, channel number and others.
Raw stream may contains PCM or DSD audio data, that compressed or not. The audio data is splitted to portions (frames). Each frame (group of frames) have a header. As rule, the meta-information contains in the header.
Should I use PCM or Auto?
If you want to be sure that PCM mode of AV equipment is used, use PCM.
Sometimes, PCM doesn't allow tranfer multichannel audio. As example, for SPDIF interface. In this case, Auto is recommended.
Also, some devices aren't compatible with Dolby Digital, and set PCM may solve the issue.
Back to top
F.A.Q. sound quality
Is PCM audio high quality?
Some of PCM formats support high quality audio. Read more...
Is PCM lower quality?
No. In TV applications PCM is uncompressed lossless format. It's high quality audio.
In audio, PCM including both low and high quality audio.
Read more...
Is PCM better than stereo?
PCM can provide stereo audio. And stereo audio may be in lossless or lossy PCM.
Read more...
Is PCM audio better than Dolby Digital?
Dolby Digital is family of size-compressed PCM audio formats. Dolby Digital formats may be lossless (by sound quality) or lossy compressed.
For sound quality:
- PCM (lossless in AV-applications) is the same as lossless Dolby Digital formats.
But in general, PCM have no sample rate, bit depth, channel number limitation; - in general case, PCM (lossless in AV-applications) is better, than lossy Dolby digital formats.
However, lossy compression allow to transmit higher audio resolution through digital audio interfaces with limited throughput (SPDIF, as example). And higher sample rates, despite lossy compression, may give sound quality advantages in some conditions. Read details...
Also channel number throughput issue may be solved via lossy compression.
| PCM audio | Dolby Digital | |
|---|---|---|
| Sound quality | Maximum (lossless) | Maximum (lossless), but worse for lossy size compression |
| More channels for limited throughput | No matter for HDMI | More channels for lossy compression for SPDIF. No matter for HDMI. |
| Lossless size compression | Yes | Yes (depend on format) |
| Lossy size compression | No | For higher channel number when throughput is limited |
What is the highest audio quality?
If we means audio resolution as quality, 64-bit float / 1536 kHz is highest quality audio for PCM and 1-bit/45.2MHz for DSD (DSD1024).
Highest quality requires lossless (bit-perfect) support for an audio data.
Read more...
What is the highest quality format for audio?
Lossless-format family is the best. Read more...
What is the best format to save music files?
To achieve the best sound quality, use one of lossless audio formats. To save hard disk space "seriously", use lossy-compressed audio formats. These formats also provides high sound quality. Lossless formats save full sound quality of original recording.
Read more...
Is PCM better than mp3?
mp3 is size-compressed PCM signal. In home theater uncompressed PCM is called as "PCM".
mp3-compressed stuff is lossy. So, using uncompressed PCM is preferable, where no requitiments to:
- data throughput via a line or
- size of file.
Read more...
What is the best PCM format?
PCM formats differ by:
- supported resolution,
- ability to lossless compression;
- compression size.
These factors should be considered in complex according to your application. Read more...
However, the best-sounding audio resolution is matter of used musical equipment rather. Read more...
Is WAV better than PCM?
PCM is audio format family. WAV is popular PCM format. Read more...
Is M4A or MP3 better?
m4a contains ALAC or AAC format. ALAC is lossless and it's technically better than AAC and mp3.
AAC is newer than mp3. And AAC developers promise better sound quality. Also, AAC supports high resolution audio.
Read more...
Is WAV better than MP3?
Yes. In contrast mp3, WAV is lossless audio format and supports high resolution.
Read details...
What are two of the most common digital audio file formats?
The author consider WAV and mp3 as most common audio formats.
Totally, in audio we have 2 basic audio formats: DSD and PCM.
Read more...
Does Youtube support linear PCM?
From technical point of view, YouTube supports data-compressed linear PCM audio.
However, in home audio-video, linear PCM means "uncompressed linear PCM". In this meaning YouTube doesn't support "linear PCM".
Back to top
F.A.Q. Dolby Digital
What is PCM Dolby Digital?
Dolby Digital if family of size-compression methods of PCM (pulse-code modulation) audio with or without losses.
Lossless compression is the same to ordinary PCM. But size-compression allow to solve issues of:
- throughput limitation of digital audio interface;
- limited capacity of digital audio mediums (optical disk, hdd).
Is PCM audio better than Dolby Digital?
Dolby Digital is one of PCM format family. Losslessly compressed formats causes lesser distortions than lossy ones. Dolby Digital supports both types of the compression.
Read more...
Should I set my TV to PCM or Dolby Digital?
When th TV has HDMI interface, it's recommended to set LPCM/PCM.
When SPDIF is used, set Dolby Digital mode.
Read more...
Which is better Dolby Digital or DTS?
DTS is one of formats of Dolby Digital family. It allow to support either lossy or lossless compression. Dolby TrueHD support higher audio resolution and channel number. See details in the table...
Back to top
F.A.Q. PCM converter
How do I convert PCM to WAV?
WAV is one of PCM format. An you can convert WAV to WAV, FLAC, mp3 and other PCM format.
Read more...
How do I convert PCM to MP3?
mp3 is one of PCM format. An you can convert mp3 to WAV, AIFF, FLAC, mp3 and other PCM formats.
Read more...
Back to top
F.A.Q. bitstream
What is difference between PCM and bitstream audio?
Sometimes, size-compressed PCM audio is called as "bitstream audio". Bitstream (bit per second) is used to easier estimation of efficiency of size compression or communication channel abilities.
Which audio is better PCM or Bitstream?
If a lossy PCM audio formats are called as "bitstream", then uncompressed PCM is better than the "bitstream". But higher sample rates of compressed audio may give advantages in sound quality.
Which is better 128k or 256k MP3?
Higher mp3 bitrate 256k keep more audio information than lower 128k one.
Higher bitrate means better sound quality (lesser losses).
Read more...
Which audio format is best 128k or 256k?
For hi-fi applications, 256k is more recommended than 128k bitrate.
In simple words, higher bitrate keep "more audio quality".
Read more...
Back to top
F.A.Q. surround
Is PCM surround sound?
PCM can provide surround sound. Read more...
Which surround sound mode is best?
PCM mode is recommended for surround and other sound. However, if you uses SPDIF hardware interface, Dolby Digital can allow transmit surround audio.
Read more...
What is PCM multichannel?
"PCM multichannel" in AV-applications is multichannel uncompressed audio in PCM format.
Is 5.1 better than PCM?
5.1 means multichannel sound signal. It may be in PCM format.
Is PCM audio better?
PCM audio one of audio formats. In TV applications it's considered as a lossless one. So, PCM provides maximum sound quality.
But, throughput of digital interfaces between audio/TV units is limited. Therefore, compression, lossy and lossless, may be required.
Is PCM Dolby Atmos?
No. It's things in different domains.
Dolby Atmos is technology to code sound object spatial location.
Sound form an audio unit to a speaker, may be sent in different PCM formats, that provide compatible phase and amplitude response.
Read more...
Back to top
F.A.Q. HDMI, digital, analog
What is HDMI audio format PCM?
HDMI is just protocol and hardware interface to transmit audio data. HDMI may transmit audio data in PCM audio format.
Does HDMI carry audio?
Yes. HDMI can transport multichannel high resolution audio.
What is optical digital audio out?
Optical digital audio output (Toslink) is one of types of SPDIF. It requere special optical cable to conection.
What does SPDIF PCM mean?
It is PCM, that is transmitted via SPDIF audio interface.
What's PCM audio cable?
PCM audio cable is any electrical cable, that allowing transmit digital audio data: SPDIF, HDMI.
Back to top
Conclusions
- PCM is way to code analog signal in digital form.
- Its bit depth depend on desirable noise level. The bit depth defined by each application.
- Sample rate is defined according analog filter primarily. To better work with analog filter, digital filtration is used.
- PCM editing and processing is easier than DSD.
- PCM may be compressed lossless or lossy.
- 44.1 kHz 16 bit may be enough in some conditions. But it is implementation matter rather.
Here test to sample quality comparison
- The MP3 Is Officially Dead, According To Its Creators
- Linear Pulse Code Modulated Audio (LPCM)
- Is MQA DOA?
- ALAC specification
- mp3 specification
- AAC specification
- CAF specification
- DTS specification
- AC3 specification
- WMA specification
- About quantization noise
- Dolby TrueHD specification
Audio Basis - articles about audio
Back to top