
Are you passionate about music and crave the clearest sound experience? The secret lies in choosing the right audio file format. Not all formats are created equal—some enhance your listening experience, while others are tailored for specific gadgets and purposes. This comprehensive guide demystifies the world of audio formats:
- Uncover the finest audio file formats for pristine sound, including WAV, FLAC, mp3, AIFF, m4a, AAC, ALAC, PCM, MQA, DSD, DSF, DFF, and SACD ISO.
- Explore the pros and cons of lossy versus lossless audio compression and how they impact your tunes.
- Learn the key distinctions between PCM and DSD formats to make an informed choice for your audio collection.
- Find out which audio formats reign supreme for Android, iOS, Mac, Windows, and Linux platforms.
- Get answers to common queries about music files and unravel the mysteries of sound file formats.
- Make the smart choice with our easy-to-follow infographic, guiding you to the best audio codec for your needs.
Achieve maximum sonic excellence. Read on to ensure your music hits all the right notes!

If you buy "AuI ConverteR PROduce-RD" (2023/12.x version) from 24 August 2023 to 24 October 2023, you will get free update to version 2024 (13.x) after its release.
- What is an audio codec and format?
- What is highest quality audio format?
- Lossy vs lossless audio formats
- Audio codec comparison
- The Purpose Behind Diverse Audio Formats
- The best music formats (codecs)
- Lossless PCM formats (codecs)
- Lossy PCM formats (codecs)
- DSD formats
- Bluetooth audio codecs
- Audio formats for iTunes
- What are the best music formats? Conclusions
- Frequently Asked Questions
![video: How to improve sound quality [Your Guide]](/pictures/videopic/sd--nK1n7Im1VKY.jpg)
What is an audio codec and format?
An audio codec is a sophisticated tool that transforms the storage format of your sounds, optimizing them for various uses.
The audio format defines the structure of sound data within a file or stream, detailing the compression methods, data blocks, and metadata organization.
At its core, sound data is a sequence of digital samples, representing the acoustic waves we perceive as music or speech. Through the magic of the best encoding, bulky sound files are compressed into manageable sizes without sacrificing quality. Conversely, the best decoder restores these sounds to their original glory. The best audio codecs masterfully makes these two processes.
Commonly integrated into audio playback devices and conversion software, audio codecs like the mp3 codec, flac codec, and aac codec are pivotal in delivering high-quality audio experiences.
Whether you're comparing audio codec types for the highest quality audio codec or seeking the best audio format for editing, understanding these technologies is key to achieving the best sound quality for your music or movies.
Back to topWhat is highest quality audio format?

Dive into the realm of high-fidelity sound as we uncover the best audio format for unmatched audio quality.
An audio codec is more than a program; it's the alchemy that transforms sound storage, enabling efficient space usage and swift streaming. Discover the inner workings of codecs here.
Imagine music as a sequence of sonic spheres, each varying in size.
These spheres can be symbolized by numbers:
"1" for small,
"2" for medium,
"3" for large,
"0" for silence.
This numeric sequence represents an acoustic waves of music: 1010123.
An encoder, a vital component of the codec, compresses the sound data, while the decoder restores it to its original state.
When the codec's magic ensures the original and processed data match, we call it a lossless codec—the guardian of full sound quality. If there's a variation, it's a lossy codec, which may alter the sound quality.
For the audiophile, a true lossless audio format represents the zenith of auditory excellence.
Back to topLossy vs lossless audio formats
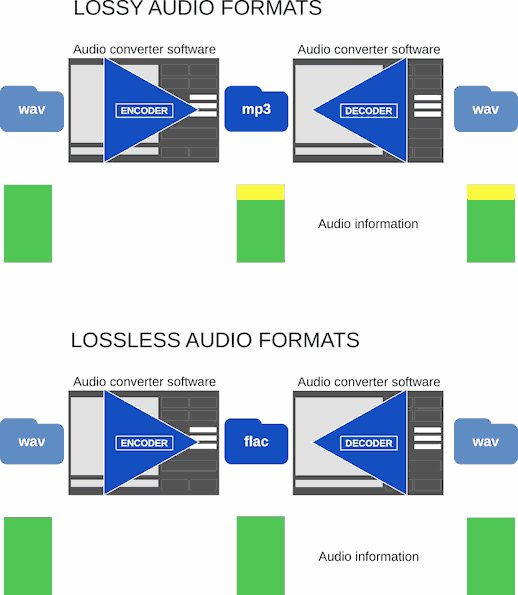
For connoisseurs of sound, certain formats stand out, offering a higher caliber of audio fidelity than others.
Sound quality is the measure of fidelity to the original recording, preserved after digital encapsulation.
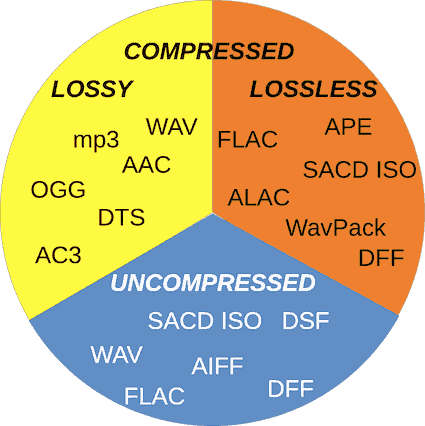
Music file formats fall into three categories:
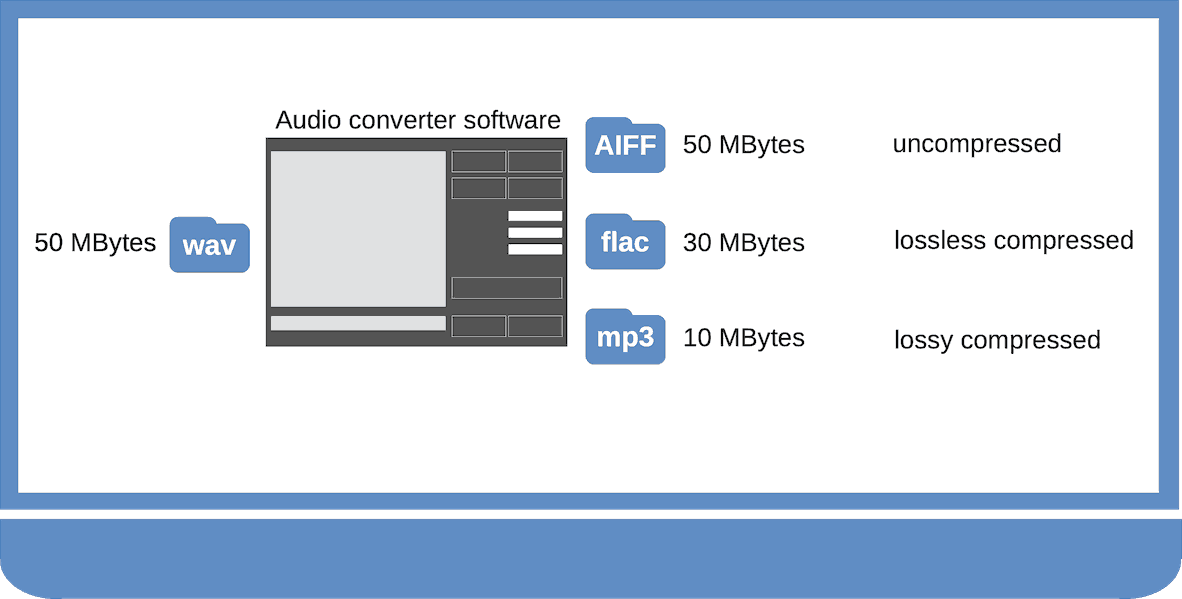
- Non-compressed: These true-to-source formats maintain the original sound without alteration, requiring more storage. Examples include WAV, FLAC (uncompressed), AIFF, ALAC, DSF, DFF, and SACD ISO.
- Lossless compressed: These formats shrink file sizes while preserving original quality, optimizing storage. Notable formats are FLAC, APE, DTS-HD Master Audio, WavPack, DFF, and SACD ISO.
- Lossy compressed: These formats reduce file sizes at the cost of some quality alteration, offering the smallest footprint. Familiar formats are mp3, AAC, MQA, DTS, and OGG.
For an in-depth exploration of lossless audio formats and their benefits, read more...
Back to top
Audio codec comparison
Compression is the art of shrinking audio files. Typically, lossy compression results in smaller files than lossless compression, but at the cost of some sound fidelity.
The highest quality audio formats are known as 'lossless'. They preserve sound integrity perfectly, ensuring the original and processed data are identical.
Lossless formats maintain the original sound without alterations, guaranteeing consistent sound quality across all lossless types. However, converting between DSD and PCM lossless files can result in minimal sound loss. Yet, with proper conversion techniques, these losses are negligible.
The best sound quality audio formats are called "lossless". They keep the sound quality the same: the original and changed sound data are the same.
![Choosing Your Ideal Music Format: A Quick Guide [Detailed insights below]](/sites/default/files/u1/best-audio-file-format-m.png)
Factors Influencing Playback Sound Quality
Playback sound quality is distinct from the audio quality of the music format itself.
While codecs slightly modify sound quality, they don't account for all changes during playback.
Playback quality also hinges on:
- the recording, mixing, and editing processes;
- losses associated with the audio format;
- the software used for playback;
- the hardware reproducing the sound.
EXAMPLE:
Adjusting the sound's resolution can impact playback quality on different software or devices.
Increasing or decreasing resolution slightly alters audible distortions, contingent on the playback system.
Thus, sometimes, modifying an audio file's resolution can enhance playback sound.
Summary: The best audio quality formats are those that retain the sound's purity. Yet, tweaking the sound resolution or format (DSD to/from PCM) might improve playback quality. Discover more...
Back to topThe Purpose Behind Diverse Audio Formats
Audio formats are crafted to address various needs:
- Delivering optimal sound quality;
- Conserving storage space on music devices;
- Providing song details (metadata: cover art, track and album titles, artist, etc.);
- Ensuring compatibility with a range of software and hardware.
The best music formats (codecs)
Selecting the Finest Music Formats and Codecs:
- In terms of modulation: DSD and PCM;
- Regarding size compression: compressed and non-compressed:
- Compressed files categorized by sound quality:
- Lossless - preserving audio integrity,
- Lossy - compact but with some quality compromise.
- Compressed files categorized by sound quality:
The sound quality is independent of the operating system (be it Android, iOS, Windows, Mac, Linux, or others) used on computers or mobile devices. Instead, it largely depends on the playback system's settings, including the operating system drivers.
Discover more:
| loss |
lossy | |
|---|---|---|
| comp |
||
| non-comp |
* MQA format can be both lossy and lossless under different conditions.
The term FLAC stands for "Free Lossless Audio Codec". A *.flac file may also serve as a container for other formats, such as MQA.
Learn more about:
Lossless PCM formats (codecs)
Lossless PCM audio formats include WAV, FLAC, AIFF, ALAC, APE, MQA, and CD-audio. They can be either compressed or uncompressed, each with its own merits.
Popular formats such as WAV and AIFF might present metadata compatibility challenges with certain audio software and devices.
When it comes to the best lossless audio format, all lossless codecs deliver identical sound quality. However, differences arise in compatibility and metadata support.
The term 'lossless' refers to compression that reduces file size without any loss in audio quality.
For instance, if an original digital audio file contains two stars (**), we could represent this as "1" for compression purposes.
By substituting "**" with "1", we halve the file size. Upon decompression, "1" is reverted back to "**", ensuring the playback audio is exactly the same as the original.
This method exemplifies 'lossless' compression, as it preserves the integrity of the audio data.
For further insights into lossless audio, read about lossless audio...
Additional resources:
Explore an Investigation of Lossless Audio Compression for an in-depth understanding.

WAV
WAV files are widely recognized among uncompressed lossless formats, though they can also store lossy compressed audio data.
This format is supported by numerous audio devices, but metadata display issues may arise with some systems.
WAV files can encapsulate DoP packed DSD audio streams, requiring specific pre-processing or hardware for playback.
Generally, WAV is suitable for editing software and extensive music libraries on large hard drives, though FLAC is often preferred for its smaller size.
WAV files have no inherent limitations on sample rate and bit depth, but standard applications cap file sizes at 4 GBytes. WAV RF64 and SONY's WAV64 formats overcome this limitation, allowing for larger file sizes.
Discover more about the WAV format and its comparison to FLAC.
AIFF
AIFF enjoys popularity as an uncompressed lossless format, compatible with many music devices, albeit with potential metadata compatibility issues.
As an uncompressed format, AIFF is recommended for iTunes users due to its metadata support.
AIFF files can also contain DoP packed DSD audio streams. AIFFs are well-suited for audio editors and music libraries, though FLAC remains a more optimal choice.
AIFF files are not strictly limited by bit resolution and sampling rate, but file sizes are typically kept under 4 GBytes. The AIFF-C lossless format is specifically designed for CD-audio tracks.
Free Lossless Audio Codec (FLAC)

The FLAC format offers lossless compression, ensuring your audio content remains unchanged while reducing file size. It boasts widespread metadata compatibility across various devices and software.
Some audiophiles prefer uncompressed FLAC for its perceived superior sound quality, although there is no conclusive evidence to support this claim. For more information, visit FLAC sound quality explanation.
Note that FLAC files are not compatible with the iTunes player. But, you can convert them to Apple Lossless format and entirely keep quality.
FLAC files can include DoP packed DSD music, similar to WAV and AIFF formats.
FLAC supports a maximum resolution of 32 bit / 384 kHz, and file sizes can exceed 2 GBytes, depending on the editing and conversion software used.
For a comparison between FLAC and WAV, read here.

Apple Lossless Audio Codec (ALAC)

ALAC is a losslessly compressed audio file format, often recommended as an alternative to FLAC for iTunes users.
CD audio
CDs store audio data in a format akin to 16 bit / 44.1 kHz WAV. This data can be transferred with full quality to WAV and other audio files using CD ripper software.
In Windows, CDs display *.cda index files indicating track positions, but copying these files does not extract audio. Instead, audio ripping software is required.
On Mac OSX, CDs show *.aiff files, which can be copied like standard audio files. However, these contain AIFF-C lossless format with a byte order inverse to standard AIFF. AIFF-C can be converted to AIFF without any loss.

Learn more about:
WMA lossless
WMA (Windows Media Audio) offers lossless compression starting from codec version 9. WMA files can be converted to WAV using the wmal2pcm utility, which may require additional installation.
The utility may be located at "c:\Program Files\windows media components\tools\wmal2pcm".
For more information on the WMA codec pack, visit Microsoft Support and the Media Feature Pack download page.
APE
APE (Monkey's Audio codec) provides lossless compression and supports metadata, with official builds available for Windows. For more details, visit Monkey's Audio.
WavPack
WavPack is a versatile lossless audio format that also supports metadata. Learn more at WavPack.
CAF (lossless)
CAF (Apple Core Audio Format) serves as a container for lossless audio formats, including uncompressed PCM or ALAC codec-compressed audio. It fully supports metadata.
For more on CAF, see the section on CAF lossy.
DVD-A [lossless]
DVD-Audio supports an uncompressed PCM audio stream in stereo (16|20|24-bit / up to 192 kHz) or 6-channel surround (up to 24-bit / 96 kHz). For a detailed reference, see this DVD-Audio paper.
DVD-V [lossless]
DVD-Video accommodates an uncompressed PCM audio stream in stereo (16|20|24-bit / up to 192 kHz) or DTS 5.1-channel surround (up to 24-bit / 96 kHz). For more information, refer to this resource.
MQA (Master Quality Authenticated) [lossless]
MQA is a high-end PCM format that delivers lossless high-resolution audio at 17-bit/96 kHz. To understand the differences between MQA and FLAC, read the definitive guide.
Back to topLossy PCM formats (codecs)

Lossy compressed formats such as mp3, aac, ogg, and others are designed to maximize the number of songs stored within the limited hard disk space of a music device or computer.
These formats strike a balance between minimizing file size and preserving audio quality. The bitstream, measured in kbps (kilobits per second), characterizes the audio information per second and determines the audio quality.
Generally, lossy files are compatible with metadata standards. While WAV and AIFF have lossy variants, they are not commonly used.
The best audio codec for a lossy file depends on various factors, but for mp3 and AAC, a bitrate of 256 kbit/s or higher is typically recommended for high sound quality.
Keep reading for details about lossy audio codecs.

How to choose the optimal bitrate for lossy formats
Bitrate is crucial for managing storage space. The goal is to find the lowest bitrate that still delivers satisfactory sound quality.
Typically, a bitrate of 256 kbit/sec or higher is recommended.
To determine your optimal bitrate, follow this guide:
- Select several lossless audio files (FLAC, WAV, AIFF, etc.) from your preferred musical genres.
- Encode these samples into mp3 or another lossy format at various bitrates.
- Listen and compare these lossy files with the original lossless ones to identify any noticeable differences in sound quality.
- For future encoding, use the lowest bitrate that you find has the least audible difference from the original.
Your equipment may determine the result of the tests.
Additional Resources:
- The Effects of MP3 Compression on Perceived Emotional Characteristics in Musical Instruments
- Music Compression Algorithms and Why You Should Care
- A Short Study on Audio Compression
- About AAC Format
- AAC Audio Playback Tests (Multichannel)
mp3
The mp3 format remains the most widely used lossy format for music downloads, balancing size and quality effectively.
AAC
AAC (Advanced Audio Codec) is a newer codec than mp3, promising improved sound quality and support for multichannel audio. Learn more about AAC's advantages over mp3 here.
WMA lossy
Windows Media Audio (WMA) is a versatile codec with both lossy and lossless capabilities, popular in the Windows ecosystem.
DTS
DTS is a format that specializes in storing compressed multichannel audio. More information can be found here.
AC3
AC3 format is known for its ability to compress multichannel audio without significant losses in quality.
CAF [lossy]
CAF is an Apple Core Audio Format container that can hold various lossy audio codecs, including AAC and mp3, while supporting rich metadata[?].
Also, see CAF lossless
MQA (Master Quality Authenticated) [lossy]

MQA is a audiophile PCM format that offers excellent compression efficiency and high-resolution audio. It’s lossless at 17-bit/96 kHz and compatible with non-MQA devices, albeit not at full capabilities. For a comparison between MQA and FLAC, and to learn more about MQA, visit MQA vs FLAC and Bob Talks MQA.
DVD-V (lossy)
DVD-Video (DVD-V) format utilizes data compression through Dolby Digital (AC-3) or DST codecs to deliver stereo or 5.1 multichannel audio, offering a balance between file size and sound quality for movies[?].
Back to topDSD formats

DSD formats like DSF, DFF, and SACD ISO (*.iso) are renowned for their high-quality audio format, utilizing 1-bit sigma-delta modulation for lossless audio reproduction. These formats are favored by audiophiles for their simplicity in digital-to-analog conversion compared to PCM.
While DFF and SACD ISO can be DST compressed, DSD content can also be encapsulated in DoP format within lossless PCM files like WAV or FLAC, ensuring the highest quality audio codec experience.
Metadata: DFF often presents challenges with metadata display during playback, whereas SACD ISO typically includes only text metadata.
Stereo and Multichannel: SACD ISO can house both stereo and multichannel versions of an album, leading to higher storage demands. To optimize space, one can extract DSF files with the desired channel number, making it the best music file format for specific playback needs.
Further reading:
Bluetooth audio codecs
Bluetooth audio codecs, such as LC3, LDAC, aptX, and AAC, are essential for enhanced sound quality and low latency in wireless devices. These codecs are crucial for catering to both music and movie experiences.
| Name | Max |
Latency | Reso |
Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAC | up to 250 kbps | |||
| LDAC | up to 990 kbps | about 250...550 ms | up to 24 bit 96 kHz |
bit |
| LHDC | up to 900 kbps | up to 96 kHz | ||
| LLAC / LHDC LL | 400 / 600 kbps | 30 ms | up to 24-bit 48 kHz | |
| AptX | up to 352 kbps | |||
| AptX HD | up to 576 kbps | 170 ms | 24-bit 48 kHz | |
| AptX LL | up to 40 ms | |||
| AptX Adaptive | 279 ... 420 kbps | 80 ms | back |
|
| AptX Loss |
lossless 44.1 kHz 16 bit, lossy 24-bit / 96kHz | introduced by Qualcom in 2021 | ||
| SBC | up to 320 kbps | |||
| LC3 | 160 kbps or 80 kbps for each of 2 stre |
multi-stream sup |
||
| Sam |
lost audio data management |
Is LDAC better than aptX?
While LDAC does not offer true lossless audio, it supports high-resolution audio up to 24 bit / 96 kHz, which may provide superior sound quality. In contrast, aptX Lossless supports CD quality at 44.1 kHz / 16 bit. High-resolution audio can theoretically offer better sound quality, but many factors contribute to the overall experience. Discover more about high-resolution audio here.
F.A.Q.: aptX codec | LDAC codec
Back to topAudio formats for iTunes
iTunes supports a range of audio formats, but it does not support FLAC and DSD files, nor can it read WAV metadata. For the best audio codec for music in iTunes, consider converting WAV or FLAC to Apple Lossless Codec (ALAC with *.m4a extension) and WAV to AIFF, ensuring metadata compatibility with iTunes.
Back to top
What are the best music formats? Conclusions
What is the best lossless audio format?
For those prioritizing sound quality of file formats, lossless options like DSF, FLAC, ALAC (*.m4a), WAV, AIFF, and CAF are recommended. DFF and WAV may present metadata compatibility issues.
What is the best lossy audio format?
When storage is a concern, compressed audio formats like mp3, AAC, and ogg are recommended, with AAC often cited as one of the best sounding among them.
Other Considerations
To conserve space on digital audio players (DAPs) and mobile phones, consider extracting stereo tracks from SACD ISOs or downmixing multichannel tracks to stereo. The operating system of your device does not affect the sound quality of playback; rather, it's the playback settings that matter. However, some operating systems, like iOS for instance, may have limitations in abilities such as supported Bluetooth codecs.
Discover Free High-Quality Music Downloads:
Frequently Asked Questions

Explore this F.A.Q. about audio file formats (codecs).
F.A.Q. audio codec [general]
Which audio codec is best?
Discover the most popular audio file formats and their extensions:
- WAV | WAV RF64 | WAV BWF (.wav)
- FLAC (.flac)
- AIFF (.aiff, .aif)
- mp3/MPEG (.mp3)
- AAC (.m4a)
- ALAC (.m4a)
- WavPack (.wv)
- DSD (.dsf, .dff)
- DSD DoP (.wav, .flac)
- MQA (.flac)
- more...
Download free music files... and find out which audio codec offers the best balance between sound quality and data compression for your needs.
What is the highest quality audio format?
What audio format is the best for sound quality? To determine the highest-quality audio format, we need to identify the format that preserves full audio quality. For audiophiles, the best options are lossless formats like WAV, FLAC, AIFF, ALAC, DSF, DFF, and others, which save original sonic data without losses. These formats are considered the best for audibility.
The debate of "which is better, DSD or PCM," does not have a definitive answer. It varies based on the implementation of equipment and the recording being played.
Considering format-resolution capabilities, WAV and AIFF offer great flexibility due to their adaptable file structure.
What is the most common audio codec?
The most common audio codecs vary based on their applications:
| Codec | Applications |
|---|---|
| WAV | Hi-res music |
| FLAC | Hi-res music |
| DSD | Hi-res music |
| mp3 | Music files, movie |
| AAC | Music files, movie, bluetooth |
| Dolby Digital | Movie |
What is the best audio format for sound quality?
The highest quality audio formats are lossless, preserving the original musical data without any losses. For hi-fi systems, these are the most recommended formats. For mobile applications, the AAC format at high bitrates (256 kbps and more) is advisable.
Discover more about audio formats offering the best sound quality...
Which is the best sound quality?
Sound quality can be defined objectively by distortion levels and subjectively by personal preference. These definitions are interconnected through psychoacoustics.
Learn more about sound quality...
Does high res audio sound better?
High-resolution audio's potential to sound better depends on the audio equipment and the recording being played back.
Explore the nuances of high-res audio...
What is the best format for music?
For music, the best audio file formats are those that offer the highest capabilities, such as lossless formats in high resolution. However, for portable audio players and mobile phones, lossy codecs like mp3 and AAC at high bitrates (256 kbps and higher) are suitable for stereo recordings.
Learn more about the best formats for music...
What is the most popular audio format?
As of April 2019, mp3 ranks as the most popular audio format, followed by m4a, WAV, and AAC. ALAC and FLAC are also widely used, with m4a serving as a container for both AAC and ALAC codecs.
What is the best sounding audio file format?
For the best audio quality, opt for lossless audio file formats.
What best audio file format for editing?
The optimal audio file formats for editing are lossless, non-compressed PCM files such as WAV and AIFF, which provide the best audio quality format for precision editing.
What best audio codec?
For the highest quality audio codec, lossless codecs like FLAC, WAV, and AIFF are preferred, regardless of whether they are compressed or not. The developer of mp3 suggests using AAC for its advanced audio encoding capabilities.
F.A.Q. MQA audio
Where can I download MQA music?
Find a comprehensive list of download sites offering MQA music here, complete with descriptions to guide you to the best digital audio format for your collection.
Is MQA better than CD?
MQA, supporting high-resolution audio, provides HD audio through MQA decoding with spectrum unfolding, potentially offering the best audio format for sound quality over standard CDs. However, the recording quality and playback system implementation are crucial in the comparison of high-res vs. CD audio.
Learn more about the comparison here.
Read more...
Is MQA better than FLAC?
While both MQA and FLAC support high-resolution audio, FLAC stands as a true lossless format, ensuring identical coded and decoded binary content. MQA, known for its high audibility, is not considered a lossless format in the same sense. Comparisons should be made based on specific recordings and playback hardware/software.
For a detailed guide on MQA vs. FLAC, see MQA or FLAC?.
Can normal CD player play MQA CD?
Yes, a standard CD player can play MQA CDs. MQA's "unfolded" format is compatible with conventional playback systems, offering a high-quality audio format even without specialized equipment.
For more details, visit here.
F.A.Q. Advanced Audio Coding
Is WAV better than AAC?
WAV, being a lossless format, technically provides better sound quality than AAC, which is a lossy format. However, at high AAC bitrates, the difference from the original WAV may be indistinguishable, making AAC a highly efficient yet high-quality audio codec for various applications.
Is M4A better than WAV?
WAV is a lossless format, while M4A can contain either AAC (lossy) or ALAC (lossless). ALAC and WAV provide identical sound quality, and at high bitrates (250 kbps and above), AAC and WAV are virtually indistinguishable, making them both excellent choices for the best music format depending on your needs.
Is AAC good quality?
Although AAC is designed as a lossy codec, it provides high quality at high bitrates, such as above 250 kbps. They making it a strong contender for one of the best audio codec for music and movies.
Is AAC the best audio codec?
AAC is a lossy codec, and technically, lossless codecs are a better choice for the highest quality audio format. However, AAC efficiently saves bitrate and offers excellent hi-fi sound quality at high bitrates, making it suitable for mobile applications and streaming.
Is 256 kbps AAC is good quality?
Yes, 256 kbps AAC is recommended for high-fidelity sound quality in stereo Advanced Audio Coding, providing a balance between file size and audio quality.
Is 320 kbps good sound quality?
Indeed, 320 kbps for stereo mp3 or AAC is very similar to FLAC and WAV at the same audio resolution, making it a high-quality audio format for most listeners.
General advice: Try different bitrates for the same original recording(s). If you cannot discern a difference from the original recording, that bitrate is sufficient for your use.
Which is better mp3 or AAC?
AAC is said to better accommodate psychoacoustical factors than mp3, making it the more recommended format. Test this by comparing mp3 and AAC files at various bitrates to the original lossless file and choose based on your audio player's compatibility or software.
Is AC3 better than AAC?
While both AC3 and AAC are lossy formats, AAC is a newer format and is considered better for high-resolution recordings.
Which is better WAV or AAC?
WAV, being a lossless format, is highly recommended for audiophile applications and supports higher sampling rates than AAC, a lossy format.
Read details...
F.A.Q. mp3
Is WAV better than mp3?
WAV is a lossless format that retains all audio information, resulting in fewer distortions compared to lossy mp3. High bitrate mp3 files, however, are very close to the lossless source file in terms of quality and are more space-efficient for mobile applications.
mp3 doesn't support sampling rates above 48 kHz and can't use abilities of hi-res audio devices.
F.A.Q. aptX
Which is better, aptX or AAC?
For Bluetooth[?], the provided bitrates are:
- AAC - up to 250 kbps,
- aptX - up to 352 kbps,
- aptX HD - up to 576 kbps.
All are lossy formats. aptX potentially offers better sound quality due to its higher bitrate. However, the real advantage depends on your specific use case and equipment.
Which aptX codec is best?
The aptX codec family includes:
- aptX [latency 170 ... 270 ms],
- aptX HD [supports 24-bit / 48 kHz with a maximum bitrate of 567 kbps, latency 170],
- aptX LL [latency up to 40 ms],
- aptX Adaptive [adaptive bitrate 279 ... 420 kbps with low latency 80 ms, backward compatible with aptX and aptX HD],
- aptX Lossless [lossless 44.1 kHz (CD-quality audio) / 16 bit or 24-bit / 96kHz lossy]. Introduced by Qualcom in 2021.
For music production or gaming with wireless headphones, aptX LL is recommended due to its low latency. For music listening, aptX HD, Adaptive, or Lossless are recommended.
Which Bluetooth audio codec is the best?
Opinions vary on the best Bluetooth audio codec. It's advisable to listen and compare codecs to form a personal opinion. Commonly recommended codecs include aptX, AAC, LDAC, LHDC, and LC3.
Study more...
Is AAC or aptX better?
For Bluetooth aptX/aptX(HD) provide bitrates up to 352/576 kbps, respectively. aptX and aptX HD offer higher bitrates than AAC, which could translate to better sound quality. However, the choice may depend on your mobile phone and headphones. AAC tends to consume more battery energy due to its higher computational requirements[?].
F.A.Q. players
What the best audio file format for iTunes?
- For optimal sound quality, use lossless AIFF and ALAC (*.m4a).
- For comparison, convert similar lossless audio files to mp3 and m4a and evaluate the sound quality.
- Bitrates of 256 kbps and above are recommended for a good balance between sound quality and file size.
What best audio file format for mobile phones, iPhone, iPad?
For devices using internal DACs, lossless PCM formats are preferable. Some external DACs support DSD. Compare the sound of your audio player app for DSD and PCM lossless formats.
What best audio format for movies?
For home music systems, lossless multi-channel sound formats like Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master Audio are recommended. DTS supports lossy compression to save hard disk space, and AC3 may also be used. Lossy compression is suitable for web and portable applications.
What best audio file format for car CD player?
If your car stereo supports FLAC orWAV files, these will provide the highest quality sound.
F.A.Q. streaming
What best audio file format for website and web?
Compressed formats such as mp3, m4a, ogg, and flac are generally recommended for web use.
For more information on online streaming, visit the Hi-Res Audio Online page and the F.A.Q. about streaming.

Audio Basis - articles about audio
Back to top