

If you buy "AuI ConverteR PROduce-RD" (2023/12.x version) from 24 August 2023 to 24 October 2023, you will get free update to version 2024 (13.x) after its release.
- What are DSD, FLAC, WAV, SACD, and others
- Is DSD better than FLAC? DSD vs FLAC sound difference
- Modulation (digital audio type)
- Bit depth and noise
- Sample rate
- Useful band for audio (music)
- Data compression
- FLAC vs DSD file size comparison
- How DAC works
- Text metadata
- Artwork metadata
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions

Back to top
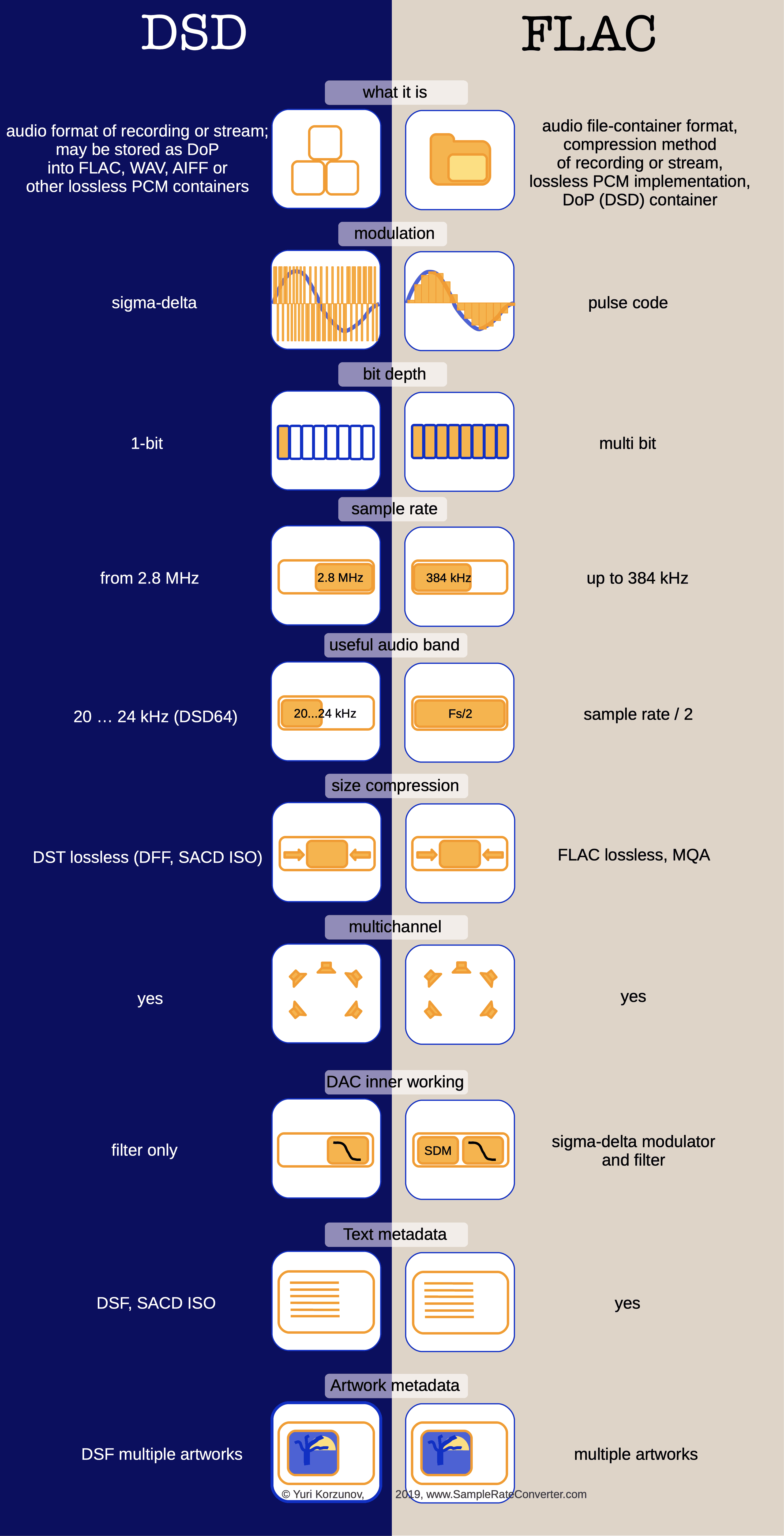
What are DSD, FLAC, WAV, SACD, and others
DSD (Direct Stream Digital) and FLAC are two ways of storing and playing digital audio. But they are very different. You can’t compare them directly. We will tell you what they are and how to compare them the right way.

What is FLAC format?
FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec) is a way of saving and playing digital audio. It has two parts:
- FLAC is a type of file that can store different kinds of audio;
- FLAC is a way of making audio files smaller without losing quality (lossless data compression).
FLAC, WAV, AIFF are ways of saving audio without losing quality. They use a method called PCM (Pulse Code Modulation). We can compare PCM with another method called DSD.
WAV and FLAC files can also store audio that uses PCM or DSD. They can make the audio smaller (compressed) or keep it the same size (uncompressed). We will explain more about this later.
What is WAV format?
WAV format is a type of file that can store and play different kinds of sound. It can use more or less bits to save the sound quality.
DSD (SACD, DSF, DFF). What is a DSD in audio?
DSD (Direct Stream Digital) is a way of recording and playing digital sound. Sony and Philips made it. DSD sample rate is how fast the sound is measured. It is much faster than FLAC and other ways of measuring sound (WAV, AIFF, etc.). Bit depth is how many bits are used to measure the sound. FLAC uses 16, 24, or 32 bits. DSD uses only 1 bit. One bit is not enough for high-quality sound. But DSD has a trick to make it work. You can read more about it below.
DSD can be saved as DoP (DSD over PCM) in a file that does not lose sound quality: FLAC, WAV, AIFF, etc..
DSD has different types: DSF, DFF, SACD disk, SACD ISO file, DoP. SACD ISO is a SACD disc's image file with .iso extension.
DSD and PCM, including FLAC, can show the same song in different ways.
For example, we can show the music as a picture with many parts (mosaic).
DSD is like the smallest squares (DSD samples). PCM is like the smallest circles (PCM samples).
We can compare 2 mosaic types (DSD and PCM) for the same picture (song).
Picture quality depends on where, how big, and what color the parts are. I.e. sound quality of the music depends on how the sound is measured.
When we change one type of part to another (change DSD to/from PCM), we lose some information. If we use good math, the quality loss is negligibly small.
What is PCM vs DSD? It is like FLAC vs DSD. To be correct, we compare how they measure the sound. FLAC is one way of using PCM.
Is DSD better than FLAC? DSD vs FLAC sound difference
The most popular DSD and FLAC comparison is listening to a single album by the same label in two different formats.
However, DSD and FLAC (PCM) sound quality comparison is a complex matter. Because there are many variables:
- recording, mixing, postproduction,
- level of recording loudness,
- playback software,
- hardware (player, DAC).
A sound difference between DSD and FLAC may be produced by a variance between these factors.

All these variables are defined by an implementation. Thus, it is impossible to say for every case: what sounds better DSD or FLAC. Because each case should be studied apart.
When we try to compare FLAC / WAV / AIFF ... other PCM and DSD album variants at home, it is easy to get sound difference due to 0.5 ... 2 dB variance between DSD and PCM circuits or software processing, in instance.
The variance may be considered as almost unlistenable as level difference. But we can get some impression of sound or audio quality difference.
So, before tests, it is necessary to compensate the level variance between DSD and PCM outputs to 0.1 ... 0.2 dB difference, approximately. It allows for avoiding an imaginary sound difference due to various levels.
Otherwise, we risk getting "better quality" for a louder DAC or DAC mode.
In instance, one person has louder PCM output and likes FLAC more. But other person has louder DSD output and prefer DSD. As a result, they can discuss "what is better" indefinitely.
And it is only one of several control goals, when the listening test is performed. And there are many details, that are invisible at first sight.
Read about hi-fi blind tests >
To DSD and FLAC format comparison:
Back to top
Modulation (digital audio type)
The main difference between FLAC and DSD is a kind of musical signal modulation. Or a kind of analog signal coding to digital form. Further, we consider the difference in the modulations.
Back to topBit depth and noise
Bit depth of DSD is reduced to 1 bit. But it causes huge quantization error noise and a low signal-noise ratio. To improve the ratio, noise energy is pushed out of the audible frequency range.
Back to topSample rate
Bit depth reduction demands frequency range reserve for noise energy pushing. The range reserve may be added by a higher sample rate.
DSD sample rates: DSD 64, DSD 128, ...
FLAC sample rates: up to 384 kHz.
Back to topUseful band for audio (music)
The range reserve causes useful DSD audio band reduction, comparing [sample rate]/2 band of PCM.
DSD is intended for audible range transmission. As rule, DSD64, has minimum noise levels in the band below 20 ... 24 kHz. Above this band noise level grows with frequency.
A higher DSD sampling rate allows for expanding this low-level noise band.
The aforementioned figures depend on implementation.
Data compression
DST (Direct Stream Transfer) is a size compression method for DSD audio stuff. It is implemented in DFF and SACD ISO files. DSF has no size compression ability.
What is size compression
We have actual issue with price of high-capacity storage devices. It's important for mobile devices, especially.
So, compression of audio data size allows more optimal use of existing storage devices.
FLAC format is intended for size compression primarily. But there is the opinion (without objective evidence, known for the author), that computing for FLAC uncompressing causes additional electromagnetic interference of a computer (or a playback device), that degrades the sound. To avoid unpacking, uncompressed FLAC is used. The FLAC is used because it contains a metadata standard way.
FLAC-container file also can contain MQA-compressed audio stuff. Such FLAC may be played back without MQA decoding.
Back to top
FLAC vs DSD file size comparison
FLAC and DSD file size comparison
| Format | 1-minute file size, Mb |
| 16 bit / 44 kHz FLAC stereo | about 6 Mb |
| 24 bit / 96 kHz FLAC stereo | about 20 Mb |
| 1-bit / 2.8 MHz DSD stereo | about 40 Mb |
Download music files for free in sample rates: DSD 64, DSD 128, DSD 256, DSD 512, DSD 1024.
Back to top
How DAC works
As rule, PCM DAC is intended for FLAC playback and based on a sigma-delta modulator and demodulator. The demodulator is a low-frequency filter.
DSD DAC can contain the filter only.
Back to topText metadata
Text metadata (album and track names, performer, etc.) contains in SACD ISO, DSF, FLAC files standard way. DFF metadata support has some issues. DSF metadata has ID3 format. It is widely supported.
Back to topArtwork metadata
SACD ISO and DFF don't support artwork metadata standard way. FLAC and DSF both can contain multiple artworks (album cover, band photo, etc.)
Back to top
Conclusion
In this article, we have explored the difference between DSD and FLAC, two popular audio formats that have different advantages and disadvantages. We have also compared their sound quality, file types, and features, and explained how to choose the best one for your needs.
The surprising answer to the question "DSD vs FLAC: Which One is the Best?" is that there is no definitive answer. It depends on many factors, such as the recording, mixing, playback software, and hardware. It also depends on your personal preference and taste. The best way to find out which one suits you better is to listen to both formats and compare them yourself.
However, we can give you some general tips to help you make an informed decision. If you are looking for a format that preserves the original sound quality without losing any data, both FLAC and DSD are a good option. FLAC can also store different kinds of audio, including PCM and DSD, and it has a standard way of adding text and artwork metadata.
Ultimately, the choice is yours. Whether you prefer DSD or FLAC, you can enjoy high-quality digital music with either format. The most important thing is to have fun and appreciate the music.
Back to top
Frequently Asked Questions
F.A.Q. sound quality
What is the highest quality audio file?
Lossless files, both PCM and DSD, are the highest-quality audio files. DSD to/from PCM files may not be transformed without losses by technical reasons. However, these losses may be minimized and comparable with qualitative resampling.
Read details...
What is the highest quality audio format?
Highest quality is provided by lossless audio formats.
Read more...
Is FLAC the best format?
FLAC is one of a lossless formats. When comparing DSD to this format, the first difference is the number of bits. Multibit resolution has better sound quality than lossy mp3 and AAC. Free Lossless Audio Codec provides data compression. But the sound quality is the same WAV, AIFF and other lossless formats. Also, FLAC allows a maximum sampling rate and bit depth limitation (32 bit, 384 kHz). One-bit Direct Stream Digital provides low noise in operating frequency range via noise shaping.
.flac file may contain lossy compressed stuff. It is encoded differently than the Free Lossless Audio Codec.
Do FLAC files sound better?
Here we'll discuss:
- do FLAC files really sound better that other files? and,
- is FLAC the highest quality or not?
FLAC files carry lossless audio. And we can be sure, that FLAC fully keeps sound quality of a source digital signal. DSD and PCM are just different modulations and it is not a matter for coded musical signal in the digital domain (when no processing, of course). However, ADC and DAC implementations may make difference between PCM and DSD formats. Read more...
Is FLAC better than 320 Kbps?
FLAC is lossless audio format. So, technically, it is better than lossy formats with 320 Kbps bitrate.
Practically, if you listen to sound difference, use FLAC format.
Read more...
Is FLAC better than MQA?
FLAC is a lossless format. As the author know, MQA is lossy format. Read details...
Is FLAC better than CD?
FLAC keeps full CD audio quality.
Read more...
Which is better AIFF or FLAC?
AIFF is a more flexible format (almost non-limited audio resolution, but some limitations with file size more than 4 GBytes). FLAC has better metadata compatibility with music devices and software. AIFF or FLAC is no matter of sound quality. Read more...
Is there anything better than FLAC?
If compare with lossless formats .wav and .aiff, FLAC has limited sampling rate and bit depth.
However, FLAC hasn't length limitation of 4 GB like ordinary WAV. WAV/RF64 solves the issue.
DSD and FLAC are compared above.
F.A.Q. WAV
Is WAV lossless?
Yes. WAV is a lossless audio format.
Is there anything better than WAV?
WAV is one of PCM formats. It is very flexible. However, you can get compatibility issues with metadata displaying and WAV subtypes, like RF64.
Metadata issue may be avoided via FLAC format using.
Which is better quality FLAC or WAV?
Both FLAC and WAV are lossless formats. WAV provides wider resolution support. FLAC provides size compression and better metadata compatibility with music devices and software players.
Sound quality is the same for both formats. However, some discussion is there.
Read details...
Is FLAC or WAV better?
We'll discuss is WAV better than FLAC? WAV is a more universal format:
- almost non-limited audio resolution,
- file size limitation (4 GBytes), which may be solved via RF64 format.
FLAC has better metadata compatibility with music devices and software. Both formats have the same sound quality.
Read more...
What does WAV mean?
WAV (Waveform Audio File Format) is a format of audio files.
Read more...
F.A.Q. DSD
What is DSD music?
DSD music is music provided in DSD format. Some DSD music samples are recorded in DSD and distributed without editing.
Read more...
What is DSF?
DSF format by SONY is one of Direct Stream Digital file formats.
Read more...
What is DSD files?
DSD files (.dsf, .dff, .iso [SACD ISO], .flac/.wav [DoP]) contain audio data in Direct Stream Digital format.
Read more...
Are DSD files better than FLAC?
DSD files are intended for DSD DAC. FLAC files are intended for PCM DAC.
If you want to get the best sound quality of your DAC, you can read how it can be done...
Is SACD better than FLAC?
SACD optical disk contains DSD audio content. You can read about FLAC and DSD comparison...
Can you hear the difference between DSD and FLAC?
In some cases, you can hear a difference between DSD and FLAC.
But it is not difference between formats as abstract items. It is difference between implementations of the technologies.
Is DSD better than PCM?
We'll consider is DSD better than PCM (including WAV and FLAC)?
What is better DSD or PCM (FLAC, WAV, AIFF, others) depends on:
- recording;
- implementation of recording and playback equipment.
Lossless PCM files (WAV, FLAC, AIFF, etc.) have similar sound quality. However, they support audio in various resolutions.
Is DSD audio worth it?
Is DSD better that other audio format? There is no single answer. Theoretically, DSD allows solving issues of an analog filter of a digital-to-analog converter. Practically, it is a matter of recording quality and equipment distortions.
Is DSF better than FLAC?
.dsf is DSD file. .flac is PCM file. Read more here...
Can DSD be converted to FLAC?
Yes. DSD may be converted to FLAC.
Read guides:
Is DSD to FLAC lossless?
When DSD is converted to FLAC, it causes losses. However, for pro-audio conversion tools, the losses (distortions) are the same qualitative resampling.
Read details...
Does FLAC support DSD?
FLAC is a container. It can contain DSD in DoP format.
Read more...
Is DSD better than CD?
DSD gives potential abilities to achieve lower distoirtions than CD. However, depending upon used hifi system, recording quality, personal issues, a listener doesn't prefer DSD.
Are DSD files better?
Despite DSD gives some audio-equipment-design advantages to achieve better sound quality, only audio device implementation defines the actual sound quality of a device. How to look for the best quality of your audio system read here...
Is DSD better than mp3?
DSD is a lossless audio format. mp3 is a lossy audio format. Thus, DSD is better in sound quality, but consume more file storage space.
Read more about audio formats...
Is DXD better than DSD?
DXD is PCM format. So, recording quality together with playback setup makes audio quality for a listener when DSD and DXD are compared.
Where can I listen to DSD audio?
You can listen to DSD music here...
What is the difference between DSD and DSF?
DSD is a sound format for high-resolution audio. DSF files contain audio in DSD format. Read more...
Is SACD better than CD?
It depends on recording and equipment. Read more...
Is MQA better than DSD?
Many factors impact to sound difference between MQA and DSD: implementation of recording and playback equipment, mix and postproduction quality of a recording. Also, it needs to remember, that MQA is lossy. But we can compare only the implementation of given audio systems. Because the small losses may not be a "bottleneck". Read more...
What is DSD audio?
DSD audio is a method of coding an analog signal in a digital form. Read more...
Is DSD the best audio format?
In theory, DSD audio system reduces number of required components. However, given system design makes actual distortion level. Quality of recording (including mixing, post-production) impacts to listenable experience.
Read details:
F.A.Q. audio conversion
Does conversion FLAC to WAV lose quality?
When audio processing is not applied, WAV converted from FLAC provides absolutely the same sound quality. See video...
Should I convert FLAC to DSD?
You can convert FLAC to DSD, when it gives actual sound advantages to your equipment. Read details...
What is DSD512?
DSD512 is a sample rate 22.6 MHz=44100 Hz * 512. Read more...
F.A.Q. play audio
What can play DSD files?
You can play DSD files via audio player software...
Alternatively, convert DSF file to FLAC and play FLAC with different players...
How do I play a DSF file?
You can play DSF files with DSD players...
Also, you can convert DSF to FLAC and play back it with any player...
- DSD vs PCM. Sound quality >
- FLAC to DSF Converter >
- DSF to FLAC Converter >
- ISO to FLAC Converter >
- DSD downloads >
- Hi-Res downloads >
- 32 bit FLAC converter >
- Uncompressed FLAC >
- 24-bit 96/192 kHz FLAC downloads >
Audio Basis - articles about audio
Back to top